
A new CDC study also found that older adults are more likely to be hospitalized for a severe respiratory virus than those aged 18 to 49 years.

A new CDC study also found that older adults are more likely to be hospitalized for a severe respiratory virus than those aged 18 to 49 years.

Infections with pneumonia send a substantial number of older adults to the hospital, much more than younger adults. Researchers are calling for new rapid diagnostic tests.

Proposed mechanisms for the association include PPI-induced acute pH dysregulation and alteration of the gut microbiome.
The price tag for an ICU stay was more than 5 times higher for pneumonia patients. Can we find an ounce of prevention?
Undiagnosed lung disease in smokers, the impact of guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia in children, and climate change and asthma attacks make headlines in the respiratory news.

Thirty minutes/day of hospital-based physical therapy reduced 30-day readmission, an important Medicare hospital performance metric.
The combined measures may help reduce hospitalizations by reclassifying CAP patients at low risk for adverse events.

Respiratory disease is the main reason why patients visit primary care practices. This brief summary highlights the latest in research and patient care.

This slideshow highlights facts and figures about the number 1 diagnostic category in primary care.

Three studies culled from the very recent literature offer insights into prevention and treatment of pneumonia in adults. Highlights in this slide show.

The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine reduced nearly by half vaccine-type community acquired pneumonia in adults aged 65 years and older.

Risk of MI, stroke, and fatal coronary heart disease remained elevated among some patients hospitalized for pneumonia up to 10 years after the index event.

Several related health concerns-including asthma, pericarditis, and pneumonia-are treatable within the primary care office.
This week: 3 questions on GI disorders, 1 Pneumonia, and the link between the brain and pain. Can you answer all 5 questions?

Respiratory symptoms are a major reason why outpatients seek medical care, and primary care physicians who treat children frequently see pneumonia. This week’s photo essay tests your knowledge of respiratory problems in kids.

Proton pump inhibitors have been associated with magnesium deficiency, pneumonia, and Clostridium difficile infection.

However, such therapy does not alter mortality, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis.
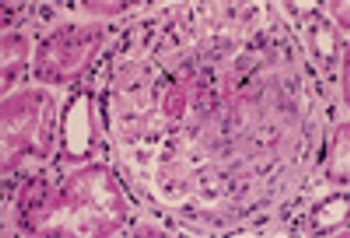
A 56-year-old was seen in the ED after 4 days of hemoptysis and intermittent left chest pain. He also complained of exertional dyspnea and arthralgias. He had been treated for “pneumonia” twice during the past month. Histories were unremarkable.

A 61-year-old man with arthritis and an 80-pack-year smoking history presented with fever, dyspnea, and productive cough of a week’s duration that did not respond to outpatient treatment with levofloxacin.

Health care–associated pneumonia (HCAP) is a relatively new term used to describe pneumonia that develops in patients who have recently been exposed to nosocomial and drug-resistant pathogens as a result of hospitalization or residence in a nursing home, for example. A recent study found that about 25% of patients hospitalized with pneumonia had HCAP, and that the mortality rate was higher in those with HCAP than in those with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
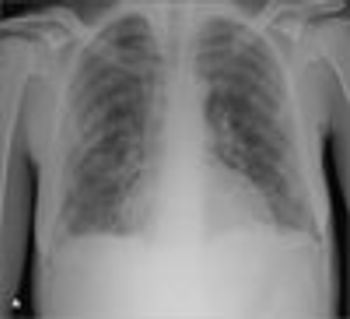
For 3 days, a 45-year-old woman with HIV infection who was noncompliant with her antiretroviral medications had cough, yellowish sputum, fever, and dyspnea. She denied hemoptysis, weight loss, or recent hospitalization. She had a long history of heavy smoking and alcohol and intravenous drug abuse.

New guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) issued jointly by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society emphasize the need for communities to adapt the recommendations to local conditions.

Given the dramatic advances in antimicrobials since penicillin was introduced, why has the mortality rate associated with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) remained essentially unchanged?

SAN DIEGO -- Rushing the decision to treat suspected pneumonia with antibiotics may lead to unnecessary treatment in a majority of cases, according to a small study reported here.

SAN DIEGO -- A potentially deadly form of community-acquired pneumonia linked to adenovirus type 14 has emerged in the Pacific northwest, according to a report presented here.