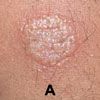
A 53-year-old woman presented to the emergency department complaining of substernal chest pain that awoke her from sleep. The chest pain was associated with left shoulder numbness, radiating to her back, and was partially alleviated with sublingual nitroglycerin. During this episode, the patient had a cough productive of yellow phlegm and one instance of cough productive of 1 tbs of bright red blood.