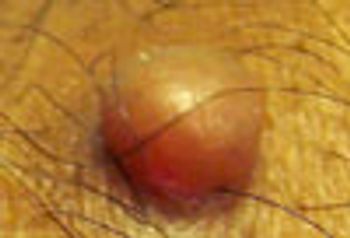
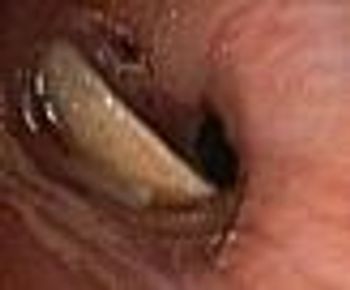
Carcinoma?; spirometry to assess chronic cough?; neurofibroma?; laryngeal neoplasm? What do you think?

Carcinoma?; spirometry to assess chronic cough?; neurofibroma?; laryngeal neoplasm? What do you think?

Take-home advice for primary physicians . . . restrict long-term maintenance erythromycin therapy to subsets of patients to protect against increases in macrolide-resistant bacteria in the broader community. Details here . . .
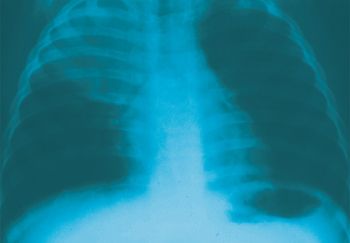
Images of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis, Wegener granulomatosis, interstitial lung disease, and other respiratory disorders show up in this photo essay.

The prevalence of chronic cough is reported to be 5% to 7% in preschoolers and 12% to 15% in older children. Diagnosis and management can present challenges.
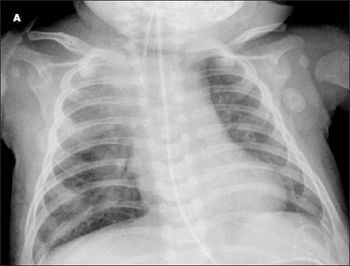
Acute bronchiolitis, COPD, giant bullous emphysema, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, and pulmonary tuberculosis may present diagnostic challenges.

Increased exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in air pollution is associated with certain immune system effects and asthma diagnosis, according to research reported the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.

Primary care physicians can take the lead in helping address these additional comorbidities in their patients with asthma.

Older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are at higher risk for plaque formation in the carotid artery, increasing their risk of stroke.

Children who use glucocorticoid inhalers to prevent asthma attacks may be on average a half-inch shorter as adults, according to a recent study.

Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) shares clinical symptoms with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) such as daytime sleepiness, headaches, and memory problems. Both the symptoms and their sequelae, however, can be much more severe in OHS. Here, guidance on what to look for and how to manage OHS.


What are the most effective ways to reduce the incidence of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?

In many parts of the country-and for people of all ages-a turn of the calendar to the winter months means more time spent indoors. For patients with asthma, however, an evening spent in front of a crackling fire may simply serve as a trigger for an attack.

A clinical nurse consultant demonstrates best practices for inhalers and puffers, with an emphasis on pediatric asthma patients.

Prof. Dominic Fitzgerald, a pediatric respiratory and sleep physician, reviews the basics about spirometry, and explains its use in children.

Recent studies have interesting implications for selecting medication and modifying asthma management. Clinician and researcher Barabara Yawn, MD, MSc provides a review-and offers insights on practical implications for primary care.
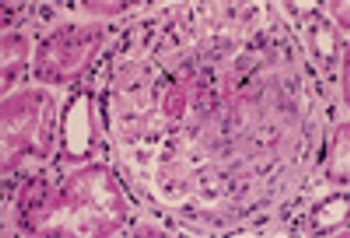
A 56-year-old was seen in the ED after 4 days of hemoptysis and intermittent left chest pain. He also complained of exertional dyspnea and arthralgias. He had been treated for “pneumonia” twice during the past month. Histories were unremarkable.

A 43-year-old African American woman presented to the emergency department with severe dyspnea, wheeze, and cough productive of white sputum. Three years earlier, she had been given a diagnosis of asthma based on symptoms of wheeze and cough; her treatment regimen included intermittent use of albuterol.

A 61-year-old man with arthritis and an 80-pack-year smoking history presented with fever, dyspnea, and productive cough of a week’s duration that did not respond to outpatient treatment with levofloxacin.

Are persons with asthma at risk for other proinflammatory disorders? Yes, say researchers from the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center in Rochester, Minn, who found that asthma is associated with the development of diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. However, there was no association between asthma and rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.

Patients who have more confidence in the effectiveness of their medications tend to be more likely to adhere to their therapeutic regimen. A recent study, which appears online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, examined whether actively promoting the benefits of a therapy can increase adherence.