
ACP: Clyde W Yancy, MD, gave a comprehensive update on a year's worth of pivotal science in treatment of heart failure. Here are the highlights.

ACP: Clyde W Yancy, MD, gave a comprehensive update on a year's worth of pivotal science in treatment of heart failure. Here are the highlights.

Research shows that increased risk of chronic disease and mortality begins below a BMI classified as obesity. The earlier we intervene with at-risk patients, the greater the chance for success.

Authors of a new study say their findings suggest bariatric surgery should be considered first-line treatment for the management of obesity in patients with type 2 diabetes.
New findings suggest that patients with asthma and type 2 diabetes who use GLP-1 RAs for diabetes treatment intensification have fewer asthma exacerbations compared to other diabetes drugs.

For frontline clinicians who care daily for patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes, a weight-centric approach to T2D, including antiobesity drugs, could help improve outcomes.
Measures of heart function and anatomy were used to assess the effects of red and processed meat on cardiovascular health; findings were reported at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021.

Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is increasing and early detection is critical. Brush up on basics with our slides.

A recent study showed lifestyle counseling in primary care was effective in preventing type 2 diabetes in long-term follow-up.

In individuals with chronic coronary disease, the presence of diabetes increased the rate of death by 38% during a 5-year follow-up period in analysis of a worldwide patient registry.
A recent meta-analysis suggests some sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor agents may protect against atrial and ventricular arrhythmias as well as sudden cardiac death in type 2 diabetes patients.
In a subanalysis of the landmark DAPA-HF trial, dapagliflozin benefits were observed in both men and women, an important finding given variable response to cardiovascular drugs among women.

COVID-19 patients with hyperglycemia on hospital admission, with and without diabetes, had increased odds of intubation, ICU admission, and mortality, according to research presented at ENDO 2021.

ENDO 2021: An investigational once-weekly insulin formulation was found as effective as daily basal insulin injection for glucose control with lower rates of hypoglycemia and less weight gain.

ENDO 2021: Obese individuals treated with semaglutide 2.4 mg vs placebo demonstrated improvements in body composition paralleling weight loss that may reduce risk for cardiometabolic disease.

Using metabolomic profiling from more than 11 000 individuals, researchers identified common pathways linking seemingly unrelated diseases that often co-occur.

Results from a head-to-head study show the investigational medication, tirzepatide, led to superior A1c and body weight reductions compared to semaglutide.

More than half of adults with obesity who received once-weekly semaglutide lost 15% of body weight, according to the recently published STEP 1 study.

A new modeling study estimates that 64% of US COVID-19 hospitalizations were attributable to at least 1 of 4 pre-existing cardiometabolic conditions.

A new review of >60 000 patients with diabetes found CGM use during the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic improved their time in range.

New research suggests obesity is responsible for 30%-53% of new type 2 diabetes cases in the US annually.
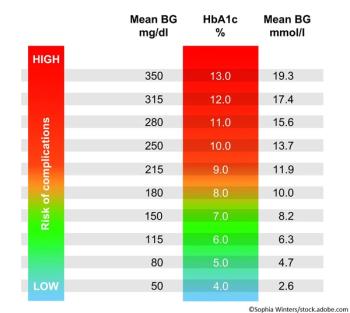
Variability in A1c during the first 2 years after T2D diagnosis is a strong predictor of CV disease; study authors note the risk may be mediated by severe hypoglycemic episodes.

Video: George Bakris, MD says over the next 3 years there is going to be an "explosion" in the number of studies we see in heart failure, diabetic kidney disease, and CV risk in general.

Director of the Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Marie McDonnell, MD, talked with our editor about 2020 studies on SGLT-2 inhibitors, insulin icodec, and more.

Compared to medication and lifestyle changes, metabolic surgery is more effective in the long-term control of severe T2D, a new study found.

Physical activity cannot compensate adequately for the negative impact of excess body weight on cardiometabolic health.