Tirzepatide at 3 different doses significantly improved glycemic control and promoted weight loss when added to titrated insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes.

Tirzepatide at 3 different doses significantly improved glycemic control and promoted weight loss when added to titrated insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Use of SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 RA therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes appears to confer hepatic protection when compared with use of DPP-4 inhibitors.
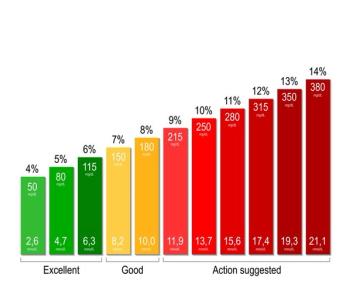
Greatest improvements in A1c, %TIR, and other glycemic parameters were seen in patients treated with ≤1 medication, in another challenge to current payer restrictions.

Integrating NAFLD as a diabetes complication to be addressed during routine cycles of care could reduce barriers to a NAFLD pathway in primary care, agreed focus group participants.

NYU endocrinologist Brian Levy, MD, offers perspective on keeping the transition from basal insulin to multiple daily injections as simple as possible for patient and provider.

Type 2 diabetes patients-and their PCPs-may have trouble moving to basal + mealtime insulin from basal insulin alone. Endocrinologist Brian Levy, MD, offers insights.

The psychiatrist-author of "Coping with COVID-19: The Mental, Medical, and Social Consequences of the Pandemic," talks frankly about the pandemic's long-term impact on American health.

Results of a new study that used early clinical surrogate markers of metabolic disease find women at greater risk related to suboptimal sleep.

The American Academy of Neurology recently issued a guideline on oral and topical treatments for painful diabetic neuropathy. Here, a concise summary for clinicians.

Glucose and insulin levels decreased after just 3 minutes of the moderate-intensity exercise, a promising finding for those with type 2 diabetes, say authors of a new study.
Coronary heart disease prevalence in the US between 2011 and 2018 saw a statistically insignificant change, from 6.2% to 6.0%, respectively.

Use of continuous glucose monitoring to assess time in target glucose range in T2D patients was evaluated in a systematic literature review covering ~14 000 participants.

Available therapies combined with new approaches that address social determinants of health and other barriers to care can help, suggests new statement.

WATCH: The FDA approval of semaglutide 2.4 mg for adults with obesity was "by far the big event in 2021," said Donna Ryan, MD. More from our look back/look ahead interview, here.
The ADA's annual update to its comprehensive evidence-based standards includes new guidance on diabetes screening, first-line therapies, and comorbid NAFLD/NASH.

CGMs have revolutionized diabetes management for patients and healthcare providers alike. This slide show summarizes the most recent enhancements.

Continuous glucose monitoring for type 2 diabetes patients is gaining exposure in the literature with positive evidence accumulating. Examples follow.

While use of insulin pumps and CGM increased over a 3-year study period for all racial-ethnic groups, the inequities were significant between White adults and all others.
Finerenone, the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, significantly reduced new-onset HF and improved other HF outcomes in the FIGARO-DKD trial.

Increases in obesity parameters significantly increased risk of incident heart failure in persons with diabetes, but not without diabetes, in a large community-based cohort study.

Get a quick look at 12 of the many FDA-approved drugs in 2021 for conditions commonly seen in primary care.

ADA 2021 Scientific Sessions recap, tests of clinical knowledge, expert interviews, and more in this roundup from Patient Care Online.

Weight loss and disease remission in T2D may differ between patients regardless of type of diet regimen chosen, say authors of a new analysis.

AHA 2021. Heart failure patients, across ejection fraction and diabetes status, reported improved QOL as early as 3 months in CHIEF-HF trial.
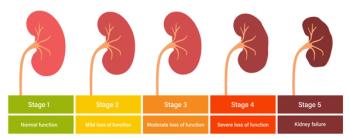
Finerenone was associated with a 20% lower risk of end-stage kidney disease among patients with T2D and CKD, according to authors of the FIDELITY analysis.