
Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.

Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.

Misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines may have eroded parents' trust in vaccination for their children, according to authors of new research.

Nonmedical exemptions from required school vaccinations accounted for more than 90% of the increase, according to the published data.

The world's first maternal vaccine against RSV in neonates and infants was approved in August. This brief slide show highlights the clinical trials that made history.

Collaboration among care team members is a key ingredient to effective support for children with disabilities and this specialist says her welcome mat is out for her neighbors.

The Pfizer product is the first vaccine indicated to prevent the 5 most common serogroups causing meningococcal disease in adolescents and young adults.

IDWeek 2023. Nirsevimab efficacy was significant across infant subgroups in preventing hospitalization for RSV-LRTI during a first RSV season.

The monovalent, singe-shot COVID-19 vaccine simplifies what used to be a complicated conversation with patients and stocking the vaccine fridge, too, says Steven Furr, MD.

Experts conclude their discussion on the efficacy and safety study of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) commenting on possible dosing strategies and key takeaways from this study.

Experts discuss the results of the safety and efficacy study of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) commenting on the adverse events observed in the test and placebo groups.

Experts discuss how infant weight related to efficacy outcomes of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), providing their clinical expertise on why this may have occurred and what improvements can be made to mitigate these differences.

Experts discuss data relating to the strains of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and how clinicians should consider them in relation to the efficacy of nirsevimab.
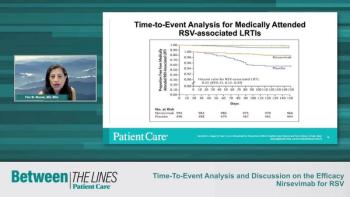
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, continue their discussion on the results of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and offer insights on how this may change therapeutic approaches in the future.

Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, and Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, discuss the initial efficacy data of the study on nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and how it compared to placebo.
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, discuss the patient population of the safety and efficacy study on nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).

Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, presents the background, objectives, and methods of a recent study on the efficacy and safety of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in late-preterm and term infants.
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, discuss the prevalence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and prior preventative gaps. They also discuss the recent FDA-approval of nirsevimab for late-preterm and term infants.
Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, and Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, introduce the objectives of their discussion and background information on Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and nirsevimab.

A daily dose of clinical news on Patient Care you may have missed.

A daily dose of clinical news on Patient Care you may have missed.

Approximately 80% of infants hospitalized with an RSV-related illness during the 2022 seasonal peak did not have underlying medical conditions, according to new study.

The AAP released 12 tips to prepare children to return to school this year, including several that focus on mental health.
The ACIP was unanimous in its recommendation for routine use of nirsevimab-alip to prevent RSV LRTD in newborns and young infants during their first RSV season.

A daily dose of clinical news you may have missed.

Nirsevimab won unanimous support from the FDA AMDAC on the vaccine's positive benefit/risk profile to prevent RSV in newborns and infants in their first RSV season.