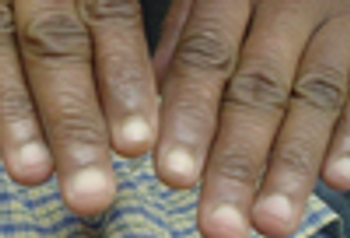
What is causing this clubbing of the fingernails, and what is it called?

What is causing this clubbing of the fingernails, and what is it called?

Ulcerative colitis has a greater impact on patients’ quality of life than physicians perceive, and the disease affects their lives even more than the impact of other chronic conditions, according to paired surveys of doctors and patients.


In many parts of the country-and for people of all ages-a turn of the calendar to the winter months means more time spent indoors. For patients with asthma, however, an evening spent in front of a crackling fire may simply serve as a trigger for an attack.
Here: 10 tips that can help you provide optimal care of your patients with MS.

Following on the heels of the obesity epidemic, a second epidemic has become apparent-sleep-disordered breathing and its effect on esophageal conditions, primarily gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Many, many primary care providers have heard the following complaint: “I gained 10 pounds and now I have heartburn/cough/worsening asthma” (take your pick). What’s going on?

A clinical nurse consultant demonstrates best practices for inhalers and puffers, with an emphasis on pediatric asthma patients.

Recent studies have interesting implications for selecting medication and modifying asthma management. Clinician and researcher Barabara Yawn, MD, MSc provides a review-and offers insights on practical implications for primary care.

A 66-year-old woman presented with a 2-day history of acute onset of redness, pain, and swelling of the right breast.

A 43-year-old African American woman presented to the emergency department with severe dyspnea, wheeze, and cough productive of white sputum. Three years earlier, she had been given a diagnosis of asthma based on symptoms of wheeze and cough; her treatment regimen included intermittent use of albuterol.

Are persons with asthma at risk for other proinflammatory disorders? Yes, say researchers from the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center in Rochester, Minn, who found that asthma is associated with the development of diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. However, there was no association between asthma and rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
Successful long-term management of asthma requires identification and control of environmental factors that increase asthma symptoms and/or precipitate exacerbations. Highlights of guidelines from the Expert Panel of the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program are presented here.

Patients who have more confidence in the effectiveness of their medications tend to be more likely to adhere to their therapeutic regimen. A recent study, which appears online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, examined whether actively promoting the benefits of a therapy can increase adherence.

Patients with asthma may be reluctant to exercise for fear of triggering an attack. You can reassure them that adequate control can allow them to participate in almost any physical activity they wish. Recommendations from the NIH offer guidance on prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm.

Primary care is demanding for a host of reasons, not the least of which is the daunting breadth of issues practitioners grapple with. One issue is evaluating the risk of suicide. Two recent studies provide some intriguing data that may change the way we practice.

In this engaging session, 5 patients with complex and difficult cases of ulcerative colitis were presented to an expert panel, which consisted of Maria Abreu, MD, Edward Loftus, MD, and David Rubin, MD. The panel moderator was Jean-Paul Achkar, MD.

This year's influenza season is approaching fast. Although the World Health Organization officially declared an end to the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic in August, the H1N1 virus is still circulating and is likely to continue to cause serious disease in infants, young children, pregnant women, and other high-risk groups.
This year’s influenza season is approaching fast. Although the World Health Organization officially declared an end to the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic in August, the H1N1 virus is still circulating and is likely to continue to cause serious disease in infants, young children, pregnant women, and other high-risk groups.
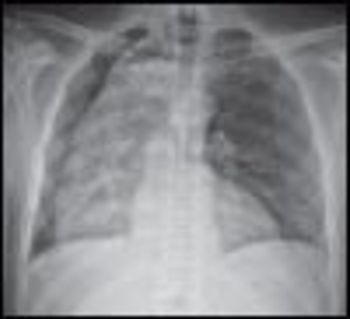
For the past year, a 52-year-old man had dysphagia, which he described as a “knot stuck in the throat” and an associated 25-lb weight loss. He denied fever, chills, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The patient had been living in the Dominican Republic until about 1 year earlier, when he moved to the United States. He had a 30 pack-year smoking history; he also had hypertension, asthma, and coronary artery disease (none of which were pharmacologically treated). He denied alcohol and illicit drug use.

Instruct patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma to discard their rescue albuterol inhalers 2 to 3 months after opening.
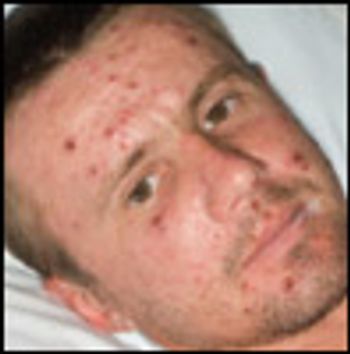
A 29-year-old Ukrainian man presents with a mildly pruritic generalized rash, which started 4 days earlier as a widespread eruption. The patient has no contacts who have a similar rash.

In adults who present with persistent cough following an upper respiratory tract infection but who have no history of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung findings are usually “normal” on auscultation.