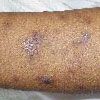
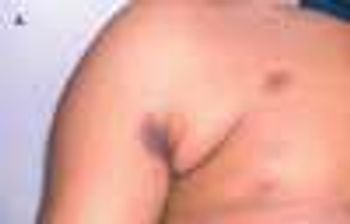
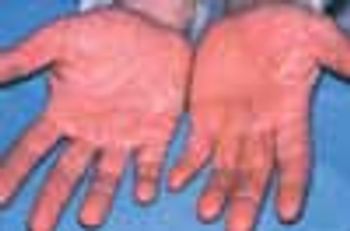
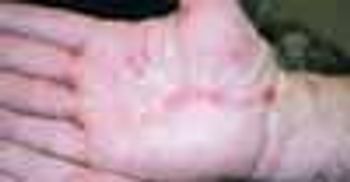
A 38-year-old man sought treatment for the intensely pruritic swellings that had arisen on his upper lip 2 weeks earlier (A). These sharply demarcated, tender, boggy, granulomatous, pustular tumefactions are kerions, write Florence Isaac, MD, of Mohammad Dossary Hospital in Saudi Arabia and Shaun Isaac, MD, of St Petersburg, Fla. The diagnosis is based on the history of acute onset, the clinical appearance of the lesions, and the demonstration of a fungus by a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of loose hairs removed from the affected area and by fungal culture. In this case, the KOH preparation revealed fungal filaments, which on culture grew Microsporum canis. A pus swab test should be performed to detect any bacterial copathogen. The differential diagnosis of kerion includes impetigo and carbuncle.