
A 14-year-old African American boy presented during the winter months with a painless, nonpruritic, periumbilical rash that had been present for approximately 1 month. Initially bluish, the rash had become dark brown.

A 14-year-old African American boy presented during the winter months with a painless, nonpruritic, periumbilical rash that had been present for approximately 1 month. Initially bluish, the rash had become dark brown.

A collage of hyperpigmented macules.

Skin signs of systemic disease: sarcoidosis, rheumatoid nodules, Muir-Torre syndrome, diabetic vasculopathy, hyperlipidemic nodules, zinc deficiency, and Sister Mary Joseph nodule.

Solitary intraductal papillomas are tumors of the major lactiferous ducts. They occur most frequently in women 30 to 40 years of age, and frequently present with nipple discharge.
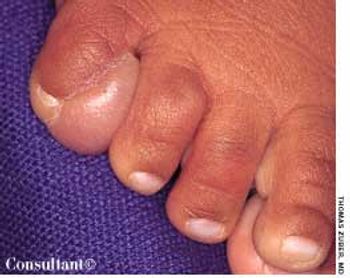
An enlarging mass was noted on the dorsum of the right fifth toe of a 2-month-old boy during a well-child examination. The firm, immobile mass measured approximately 1 cm in diameter. A congenital abnormality was suspected; the patient was referred to a plastic surgeon for consultation.
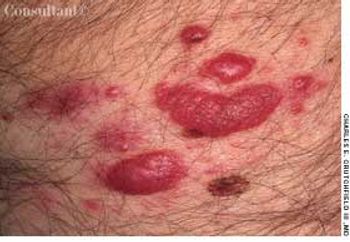
A 51-year-old man presented with red, mildly pruritic papulonodules that had erupted on his face approximately 5 weeks earlier. The clinical appearance suggested cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia.

Sclerosing adenosis most commonly occurs as multiple microscopic foci, although occasionally it presents as a palpable mass.
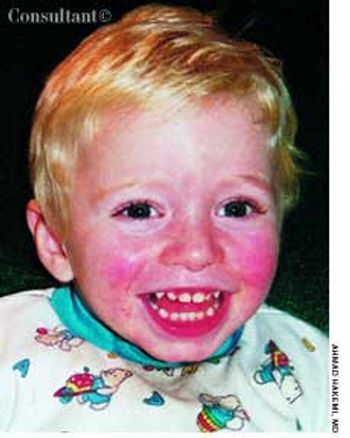
The parents of a 2-year-old sought treatment for a rash on their son's face. The child had had a low-grade fever for 3 days before the rash erupted. An intermittent lace-like rash was beginning to develop on the extremities. The patient was otherwise asymptomatic.
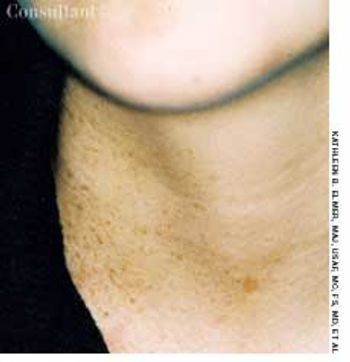
A 17-year-old girl sought evaluation of multiple face and neck nevi. The lesions had been present at birth and were becoming darker as the teen grew older. She reported no family or personal history of skin cancer or dysplastic nevi.
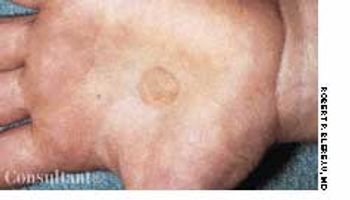
Identical circular, chocolate-colored spots developed on a 4-year-old boy's palms 2 weeks ago, according to the child's mother. The sharply demarcated, macular lesions were asymptomatic.
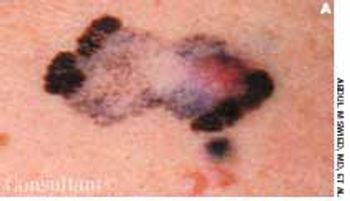
An 83-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presented with a 4-day history of mental status changes, slurred speech, and difficulty ambulating. He reported a lack of appetite and weakness of several days.
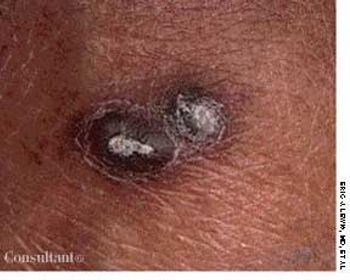
Extremely itchy, crusting nodules appeared on the arms and legs of a 42-year-old woman who was undergoing renal dialysis.
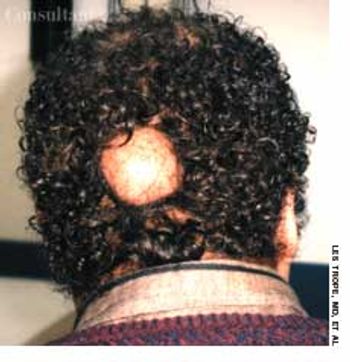
A painless swelling on the dorsum of the scalp had been present for many years in a 36-year-old man. An increase in the size of the lesion prompted the man to seek medical evaluation.
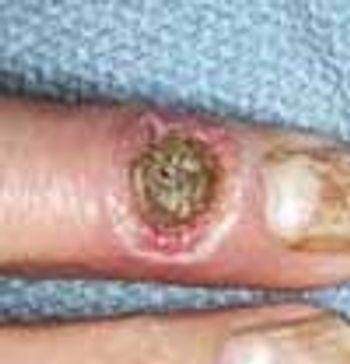
Cutaneous manifestations develop in approximately 30% of persons with diabetes. Premature atherosclerosis is a common complication of the disease that can cause peripheral infarction, ulceration, and necrosis.

Pain and pruritus of the neck and upper chest began to bother a 43-year-old woman several hours after she put on a new copper necklace. Vigorous scratching of the affected area caused excoriation of the skin, which can mask the eruption and complicate diagnosis.
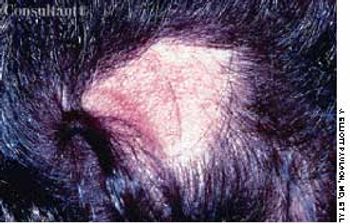
A 50-year-old man had been hospitalized for 27 days, 12 of which he spent comatose, lying on his back. A few days after discharge, he noticed a bald spot on the back of his head. The 2.5 × 3-cm area of alopecia was in the occiput, and the affected portion of the scalp was mildly erythematous.
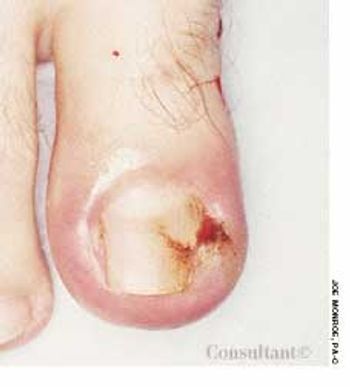
A 15-year-old experienced pain in her toe, particularly when pressure was applied to the foot. An ingrown toenail was the cause of her discomfort.
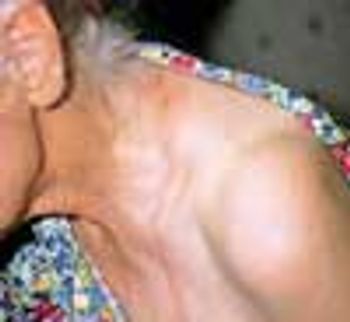
A 70-year-old woman was bothered by a pruritic, reddened site on her left shoulder. The lesion progressed with a linear, erythematous eruption leading to her axilla and caused tender adenopathy.
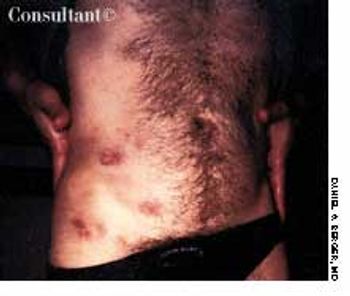
A 39-year-old man with HIV infection was being treated with antiretroviral therapy. He now sought help for multiple 2- to 3-cm violaceous papules on his right hip and the right lower abdominal area. A biopsy specimen showed intense, atypical lymphocytoid and monocytoid cells with prominent nucleoli, hyperchromatism, and bruised nuclei.
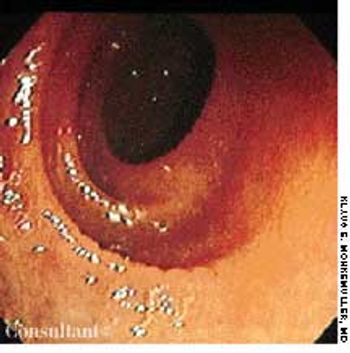
Progressive weakness and fatigue for the past 6 months prompted a 43-year-old woman to consult her physician. She denied diarrhea, melena, hematochezia, cough, fever, and night sweats. Her skin and conjunctivae were pale.

Consider this diagnosis when a patient presents with a history of rapid, diffuse hair loss. Telogen effluvium affects the entire scalp, but the crown and bitemporal areas may appear to be mainly involved if there is associated androgenetic alopecia.
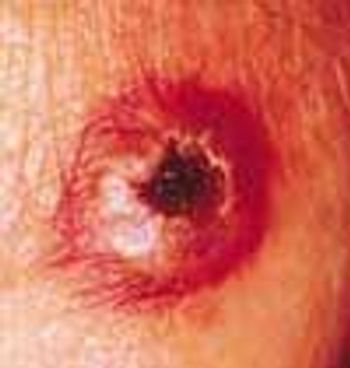
This rare condition affects both men and women. The average age at onset is 53 years. The lesions are deep brownish red to purple papules, nodules, and plaques. Blisters and ulcers also can occur.
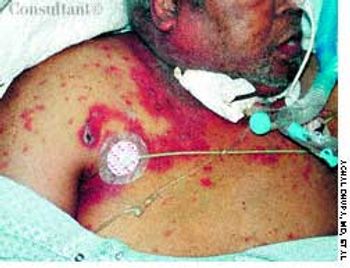
A 72-year-old morbidly obese man who had diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital from a nursing home with a fever of 4 days' duration. A tracheostomy had been performed 3 months earlier for respiratory failure. The patient was being treated with corticosteroids for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
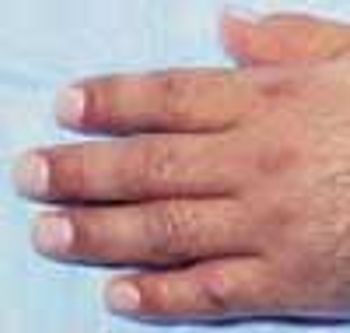
A 44-year-old man sought relief from severe pain, swelling, and restricted radiocarpal and digital motion of his left hand. Four months before, he had suffered a fracture of the distal radius metaphysis (Colles' fracture), which was treated by closed reduction with long-arm cast immobilization for 6 weeks.
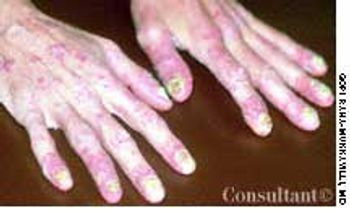
A 38-year-old woman had become increasingly depressed by worsening psoriasis in conjunction with a flare of arthritis in her hands and fingers. The patient complained that she could not function optimally and that her quality of life had diminished.