
Norovirus is the leading cause of acute gastroenteritis among children younger than 5 years.

Norovirus is the leading cause of acute gastroenteritis among children younger than 5 years.

The Department of Health and Human Services Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents has issued updates of its recommendations.

Mental illness is a risk factor for HIV infection. It brings a number of behavioral correlates that put patients at risk for getting infected. As HIV infection worsens, it begins to affect the brain, and cyclical relationship between the disease and mental illness begins.
Antidepressants and pre-term delivery; annual BP check?; stroke before age 50; niacin questioned; incretins and pancreatic disease

In some patients who are HIV-positive, combination antiretroviral therapy therapy started as soon as possible may preserve immunity and lead to a so-called functionalcure.

Elevated levels of the biomarker C-reactive protein in patients with HIV infection increased the risk of MI approximately 2-fold.
An obese woman in her thirties with a history of fibromyalgia syndrome, depression, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and diabetes mellitus presents to her local emergency department with 1 week of gradually worsening midline back pain.

Rivaroxaban rejected;HIV cure; EHR complaints; primary care errors; patient safety imperatives.

Breakdowns in the clinical encounter were related to history taking, physical examination, and ordering of diagnostic tests and

Antiretroviral treatment commenced within 30 hours of birth and continued until age 18 months.

This study confirmed the usefulness of testing on the basis of a decreased long-term incidence of ulcer bleeding.

The mechanisms and effectiveness of probiotics in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease are emerging.
Images of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis, Wegener granulomatosis, interstitial lung disease, and other respiratory disorders show up in this photo essay.

HIV-positive veterans had a 48% increased risk for acute myocardial infarction compared with uninfected veterans.
Does this look like melanoma? Which is not true of Löfgren syndrome? Yoga and Afib; what cause of mental confusion? Skin lesions and HIV.. . . See if you can answer this week's quiz questions.

The prevalence of chronic cough is reported to be 5% to 7% in preschoolers and 12% to 15% in older children. Diagnosis and management can present challenges.

Ketorolac is a good option for relieving pain in patients with sickle cell disease, but there is a problem with children.
Diabetes progress; folic acid and autism; acupuncture and allergic rhinitis; depression and shingles vaccine; HMP virus alert.
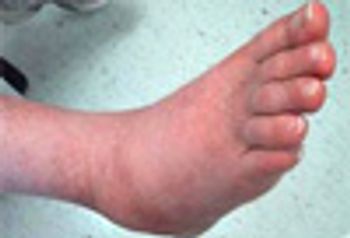
MS sex ratio, Charcot neuroarthropathy, antibiotic error, obesity and exercise.

Approximately 25% of those infected with HIV are unaware of their positive status. The USPSTF says universal screening can help reduce disease burden.
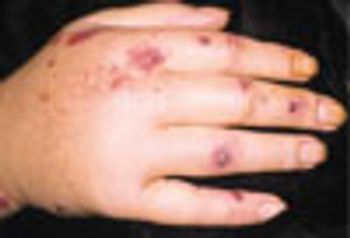
Edema of the hands has numerous etiologies: leukocytoclastic vasculitis, puffy hands from HCV infection, DVT, lymphedema, trauma

Millions of years of life have been saved by antiretroviral therapy. For more lives to be saved, for more years of life to be gained, patients and doctors need to be aware of the risk of HIV infection and to be amendable to screening.
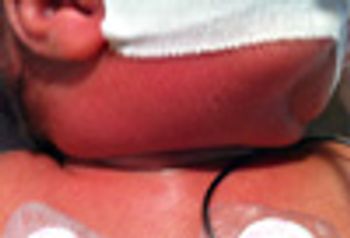
The patient had right submandibular swelling with inflammation and induration up to the nape of neck. Ultrasonography showed multiple enlarged lymph nodes with soft tissue swelling. What's your diagnosis?

This study ought to put concerns about handling and administration of donor feces to rest: the cure rate in this study of fecal microbiota transplant for recurrent C difficile approached 95%.

What are some of the more common side effects of antiretroviral therapy, and what can the primary care physician do to help manage these effects? In this podcast, infectious disease expert Rodger MacArthur, MD, offers insights and points readers to updated comprehensive guidelines.