
Frequent coffee drinkers have a lower risk than those who drink little or no coffee, of death related to heart and respiratory disease, stroke, and infections.

Frequent coffee drinkers have a lower risk than those who drink little or no coffee, of death related to heart and respiratory disease, stroke, and infections.
Acanthosis nigricans is a nonspecific increase of the thickness of the prickle cell layer of the skin and most commonly seen in obese persons.

Prenatal and Postpartum Depression Not Limited to Mothers
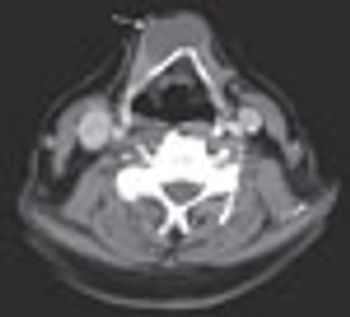
For several years, an asymptomatic mass had been growing on the neck of a 54-year-old-man. Physical examination revealed a firm, nontender mass located slightly left of midline at the level of the hyoid bone.

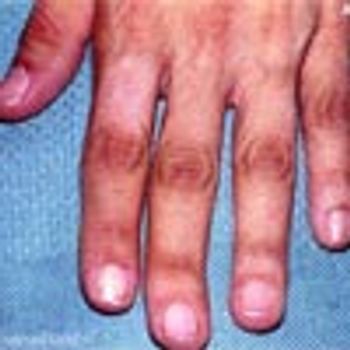
A 16-year-old boy with asymptomatic, hyperpigmented, hairy lesion on his left upper back. The pigmentation, first noted 5 years earlier, had progressively spread across his torso. The coarse and dark hair confined to the hyperpigmented area had appeared at age 13 years. Medical history uneventful. Review of systems showed no abnormalities. No family history of similar skin lesions.

A 71-year-old African American man presented to the emergency department (ED) with chest pain, dyspnea, and hemoptysis. He had had a few ED visits for similar symptoms within the previous 4 weeks.

A 36-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with loss of vision in the right eye that had initially involved the peripheral field and progressed over 2 months to the central and nasal fields. During this period, she also had headaches, vomiting, and generalized weakness. She had had amenorrhea for 1 year.

Intensive control of blood glucose levels reduces the development and progression of certain microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes but does not reduce cardiovascular risk, according to the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) study investigators.

For every recognized case of celiac disease, 8 more remain undiagnosed. The reason for this disparity is contingent on the varying presentations of the disease.

A 73-year-old man presents for follow-up after having sustained a wrist fracture aboard a cruise ship.

A 77-year-old man of Japanese ancestry with a history of well-controlled hypertension was seen in the morning for a routine examination. His blood pressure was normal as were the results of a complete blood cell count and liver function tests. About 6 hours later, he presented to the emergency department with acute abdominal pain accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills. He denied headaches, palpitations, and diaphoresis.
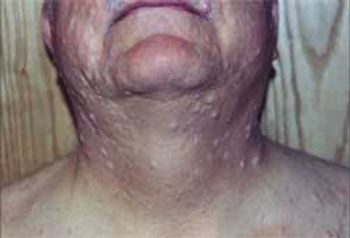
During a routine physical examination, multiple, randomly distributed, fleshcolored nodules were noted on the trunk, arms, and face of a 62-year-old man. The lesions measured 0.5 to 1.0 cm and appeared slightly pedunculated. The patient had had the lesions since he was a teenager; they were not painful. He also had hypertension, for which he was taking lisinopril (20 mg once daily).
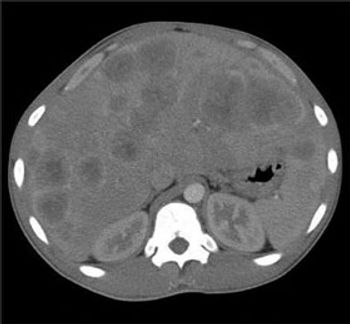
Right upper quadrant pain of 24 hours’ duration prompted a 20-year-old man with a history of gastritis to seek medical attention. The pain was sharp and nonradiating, with no alleviating or aggravating factors. The patient occasionally consumed alcohol and regularly smoked cigarettes (tobacco and marijuana). He denied nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and diaphoresis. Right upper quadrant pain of 24 hours’ duration prompted a 20-year-old man with a history of gastritis to seek medical attention. The pain was sharp and nonradiating, with no alleviating or aggravating factors.

A 77-year-old woman is brought for evaluation by her family. The patient had previously been alert and active; however, for the past week, she has been difficult to arouse and, when awake, has been delusional and has behaved abnormally. In addition, for the past 2 weeks, she has complained of abdominal discomfort related to constipation.

Levothyroxine is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of hypothyroidism as well as the suppression of thyroid neoplasms.1 Most patients with hypothyroidism require lifelong therapy with levothyroxine; therefore, the likelihood of drug interactions is high.

My patient is a man in his early 70s who complains of lack of strength. His testosterone level is low, and his B12 level is low-normal.

A 28-year-old woman presents with milky discharge in both breasts and throbbing occipital headaches of 4 months' duration. The headaches begin gradually, do not radiate, and have no apparent triggers or relieving factors.

Pain is a significant public health concern. In a prevalence study conducted in Australia, 17% of men and 20% of women reported chronic daily pain. A US study found that 13% of the total workforce had lost productive time during a 2-week period because of a pain condition. Headache, back pain, and arthritis pain headed the list of causes.

The recent "Consultations & Comments" exchange titled "What Cause of Cold and Flushing in a Basketball Player?" (CONSULTANT, November 2007) attracted my attention.

A 62-year-old man presents with painful cramps in his left lower leg that began about 6 months earlier and have recently become more frequent. The cramps occur with vigorous walking and cease when he stops for several minutes.

Nephropathy develops in about 30% of patients with diabetes. Screen for albuminuria at the time type 2 diabetes is diagnosed and within 5 years of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.

Determining the cause of generalized weakness can be a daunting task, since the differential diagnosis is vast. An overall approach to the patient who complains of generalized weakness is presented in our article

The differential diagnosis of generalized weakness is enormous; it includes disorders at all levels of the neur-axis. A variety of electrophysiological, pathological, radiographic, and other laboratory studies may be indicated depending on the specific diagnostic possibilities; costs can be controlled if such investigations are selected judiciously.

Identifying the cause of a persistent, asymptomatic aminotransferase elevation can be challenging. The possible diagnoses are many and varied. To narrow the differential, begin with a detailed history.

Treatment of hypertension can minimize both microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes and helps prevent nephropathy and cardiovascular events.