
Ulcerative colitis has a greater impact on patients’ quality of life than physicians perceive, and the disease affects their lives even more than the impact of other chronic conditions, according to paired surveys of doctors and patients.

Ulcerative colitis has a greater impact on patients’ quality of life than physicians perceive, and the disease affects their lives even more than the impact of other chronic conditions, according to paired surveys of doctors and patients.
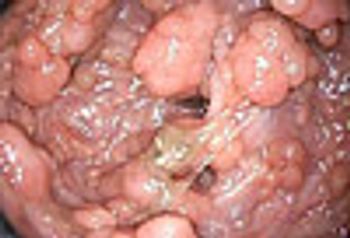
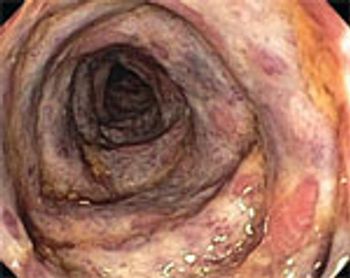
Diagnostic colonoscopy revealed innumerable polyps carpeting the mucosa from the rectum to the cecum. Endoscopic findings and family history were most consistent with familial adenomatous polyposis.
Patients with IBD may have discomfort for 3 to 5 years before a diagnosis is made. Many are treated unsuccessfully with antibiotics, anti-spasmodics, or narcotics. Here, read 5 important tips, plus a bonus point, to help streamline diagnosis and management.
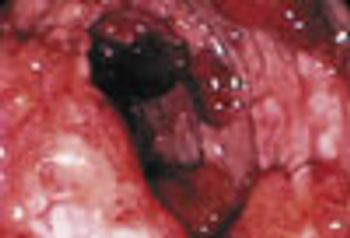
How best to manage ulcerative colitis? Here: highlights from guidelines from the American College of Gastroenterology on assessment, treatment, indications for surgery, and cancer surveillance.

A diet high in fats and protein increases the risk of developing ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, researchers found. Hou and colleagues performed a systematic review to evaluate the association between diet and risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)

Despite a lower prevalence of traditional risk factors-such as hypertension and diabetes-patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have a higher incidence of stroke, said researchers at the University of Miami.

Does upper endoscopy affect the diagnosis or management of adults with colitis? No, say investigators from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, although the procedure is routinely performed in children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) of the colon.

Quality of life in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a key focus of research presented at the 2010 Advances in IBD conference in Hollywood, Florida. Two of the top abstracts address social isolation and patient adherence to medication regimens among teenagers with IBD.

Ulcerative colitis affects about 500,000 persons in the United States and accounts for more than 30,000 hospitalizations and 1 million workdays lost each year. The exacerbations and remissions that characterize the clinical course of the disease can make its management particularly challenging. What is the optimal approach to treatment? And which agents are most effective for maintenance therapy?

More than 1000 clinicians and researchers from all over the world will gather in Hollywood, Florida, this week for the 2010 Advances in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation’s Conference. The featured speaker is Jean-Frederic Colombel, MD, Professor of Hepatogastroenterology at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Lille, France, who will discuss management strategies to improve the quality of care of patients with IBD.

For every recognized case of celiac disease, 8 more remain undiagnosed. The reason for this disparity is contingent on the varying presentations of the disease.

Read the details from 3 unique cases on GI disorders: dieulafoy lesion, colovesical fistula, and intussusception.
A 61–year–old man presented to the emergency department with diffuse lower abdominal pain, nausea, and severe diarrhea (20 episodes within the past 12 hours). His symptoms began the night before and had gradually worsened. He denied fever. His medical history was significant for hypertension.

A 22-year-old woman has had chronic nausea, emesis with green vomitus, and diarrhea for the past 10 months. The diarrhea is frequent (about 3 to 8 times daily) and does not resolve with starvation.

A 52-year-old woman presented to her primary care physician complaining of a nonproductive cough and dyspnea on exertion. These symptoms had a subacute onset over 4 weeks before her initial visit. She denied fever, sputum production, hemoptysis, chest pain, palpitations, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. She did not have any known sick contacts.
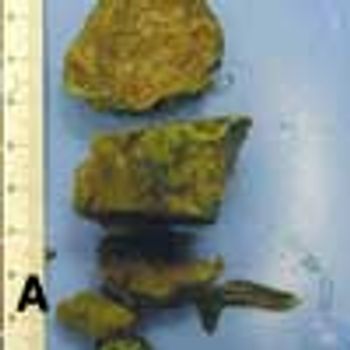
Phytobezoars commonly develop in the distal small bowel, where the lumen is narrow. Prevalence is higher after partial gastric resection.

ABSTRACT: In patients with jaundice and normal liver function, the cause of hyperbilirubinemia is an isolated disorder of bilirubin metabolism. In patients with hyperbilirubinemia who have abnormal liver enzyme levels, hepatocellular disease must be differentiated from cholestatic liver injury. In general, if the cause of jaundice is global hepatocellular dysfunction, the serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels will be predominantly elevated. If the cause is cholestasis, the serum alkaline phosphatase and gγ-glutamyl peptidase levels will be elevated. In most patients, imaging studies will be needed. The initial workup should include abdominal ultrasonography, which can identify dilated intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary ducts as well as findings that may suggest cirrhosis or signs of portal hypertension, including splenomegaly and ascites.

ABSTRACT: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is characterized by abdominal pain or discomfort, bloating, and constipation or diarrhea; the pain is typically relieved by defecation. The diagnosis is not one of exclusion; it can be made based on the answers to a few key questions and the absence of "alarm" symptoms. Fiber therapy, the elimination of particular foods, and regulation of bowel function can help relieve symptoms. Tegaserod or polyethylene glycol can be used to treat IBS with constipation. Loperamide and alosetron are of benefit in IBS with diarrhea (although the latter carries a small risk of ischemic colitis). Low-dose tricyclic antidepressants may be used to treat the abdominal pain associated with IBS. Probiotic therapy or rifaximin may help reduce bloating. Psychological therapies seem to improve well-being in patients with IBS.
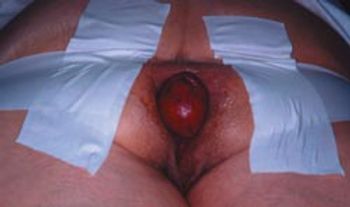
A 75-year-old woman had a 1-year history of an anal protrusion, bloodstained mucus discharge, and anal incontinence of flatus and loose stools.