
GI specialists call for more systematically developed criteria for IBS diagnosis and often rely, like their primary care colleagues, on a process of exclusion.

GI specialists call for more systematically developed criteria for IBS diagnosis and often rely, like their primary care colleagues, on a process of exclusion.

Recurrent C difficile requires pulse vancomycin therapy; fecal microbiota transplant shows promise.

Progressive weakness, confusion, and decreased oral intake preceded hospital admission for this 73-year-old man with a history of Parkinson dementia and resection for esophageal adenocarcinoma. The real problem, seen here, was revealed on a chest x-ray film.

A new study validates online delivery as an effective means of promoting dietary adherence in celiac disease, and this method may prove effective across diets for patients with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes.
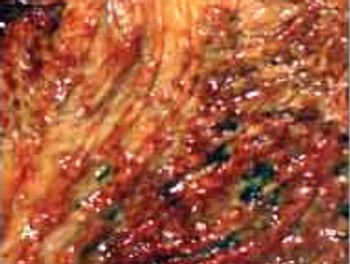
Many common GI disorders are seen in the primary care setting. This compact slide show provides visual presentations of a range of these vexing problems.

The American College of Gastroenterology's last update to their gastroesophageal reflux disease guideline was published in 2005, so this February's new synthesis of more current treatment standards is welcome.

The rate of diagnosis for acute kidney injury in hospital admissions is higher with the use of high-potency statins than with low-potency statins, according to a retrospective observation analysis.

The mechanisms and effectiveness of probiotics in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease are emerging.
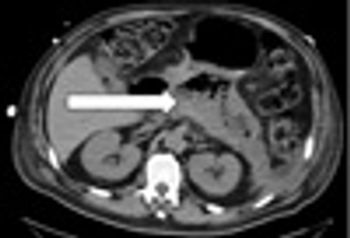
Emphysematous pancreatitis is a rare form of necrotizing pancreatitis. Free air within the pancreatic parenchyma is typically attributed to infection.

Researchers concluded that psychological factors might contribute to the development of this disorder but not ulcerative colitis.

The goals of therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disorder include inducing and maintaining a steroid-free remission, preventing and treating the complications of the disease, minimizing treatment toxicity, achieving mucosal healing, and enhancing quality of life.

These agents remain the mainstay of therapy for the majority of patients with the disease.

They are similar chronic inflammatory diseases with causes unknown, and recent clinical and genetic evidence supports an intertwined pathogenic relationship.

Therapy for ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease has been transformed with the introduction of anti–tumor necrosis factor treatment, according to University of Miami authors.
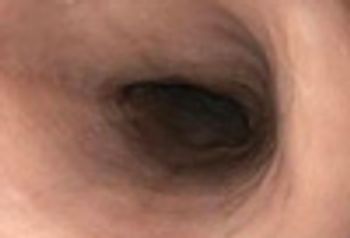
EoE is a chronic, immune/antigen-mediated esophageal disease. Clinical symptoms reflect esophageal dysfunction; histology is characterized by eosinophil-predominant inflammation.

(AUDIO) There are disparities in the sensitivities and specificities of glucose and lactose hydrogen breath tests used to diagnose small intestine bacterial overgrowth and to distinguish patients with irritable bowel syndrome from healthy individuals. Just how useful are these tests? Insights from an expert here.

Several classes of drugs seem to have positive effects for patients with GI disorders--including NSAIDs, anticonvulsants, alpha-adrenergic agents, neuromuscular agents, and antidepressants. Details here.

(AUDIO) Here, Christina Surawicz, MD, describes an organized approach to the evaluation and management of patients with chronic diarrhea.

Here: an update on the challenges of detection, diagnosis, and management of celiac disease and non–celiac disease and the importance of gluten sensitivity.

(AUDIO) According to the Centers for Disease Control, more than one-third of US adults are obese. The CDC also estimates that as many as 1.4 million Americans suffer from inflammatory bowel disorder. So is there a link?

Are you making the most out of your patients’ office visits? If you are not listening effectively, the answer is no, said Douglas A. Drossman, MD, at the American College of Gastroenterology 77th Annual Scientific Meeting in Las Vegas.

The number of patients who are dying because of upper GI bleeding has decreased over the past 2 decades, according to a study reported at the American College of Gastroenterology 77th Annual Scientific Meeting.

Patients who have chronic constipation may be at increased risk for colorectal cancer and benign neoplasms, researchers reported at the American College of Gastroenterology 77th Annual Scientific Meeting. In addition, new colonoscopy surveillance guidelines have been issued.

(AUDIO) What is the natural history of systemic corticosteroid therapy in ulcerative colitis? Insights here from Dr Nabeel Khan, Assistant Professor of Medicine in Gastroenterology & Hepatology at Tulane Medical Center-author of a new study on this topic.

Despite warnings and concerns, the evidence points to this bottom line: PPIs are relatively safe over the long term.