
There is not enough evidence to assess the benefit or harm, according to an update from the U S Preventive Services Task Force.

There is not enough evidence to assess the benefit or harm, according to an update from the U S Preventive Services Task Force.

This case focuses on duplicate therapy resulting from the use of prescription medications, which can result in serious adverse effects.

Potassium, an important component of blood pressure regulation, has been relatively forgotten.

Any antihypertensive agent, but especially ACEIs, may cause hypotension if not discontinued in the perioperative period.

Aldosterone has significant effects on vascular function and can decrease flow-mediated vasodilation.

Equivalent energy expended while walking vs running translates into comparable risk reduction for incident hypertension, elevated cholesterol, and diabetes.

A large-scale hypertension program was associated with a significant increase in hypertension control compared with state and national control rates, according to a recent JAMA study.

Nonadherence to antihypertensive drug therapy increased risk of stroke, hospitalization for stroke and stroke-related mortality.

Mid-life hypertension is a risk factor for cognitive decline. A 10 mm Hg rise in systolic pressure led to an intermediate cognitive decline in 7% of the cohort on follow-up.

At the ASH meeting, one could get a pretty good sense of where the beta-blocker hypertension debate is headed.
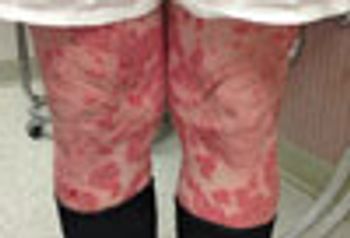
Adult-onset psoriasis is uncommon without a precipitating factor. In this patient’s case, an oral beta-blocker precipitated the psoriasis.

Yoga practice resulted in a 3-4 mm Hg decline in systolic BP at 24 weeks and a 2-3 mm Hg decline in diastolic BP on 24-hour ambulatory monitoring.

Awareness of this major health problem is on the rise, as evidenced by numerous recent reports about important new study findings.

The number of people who require 2 or more antihypertensives to reach target blood pressure is on the increase. So, simply stated, what goes best with what? The 2013 ASH meeting offered some good suggestions under the heading of “Within Class Differences.”

HIV-infected patients are undertreated for hypertension and at higher risk for cardiovascular complications than age-matched controls.

Lowering blood pressure saves lives and primary care practice is where treatment for hypertension begins.

Resistant hypertension requires aggressive treatment with multiple drugs. Spironolactone is a key addition to the regimen.

Hypertension in hospitalized patients is best treated conservatively.

More about the current move away from beta-blocker therapy for hypertension as discussed by speakers at the 2013 ASH annual meeting. Following are some more of the key points, including a discussion of so-called beta-blockers "plus."

ASH 2013 has uncovered 2 glaring gaps in the management of people with sleep disorders (OSA as well as others) and appropriate care after a stroke. Both cohorts frequent primary care practice.

Patients with resistant hypertension and hypertensive patients prone to hyperkalemia are on the rise. They are not easy to care for, but certain “tricks of the trade” can help. Details here.

The meeting's goals are to increase understanding and, perhaps, find a cure.
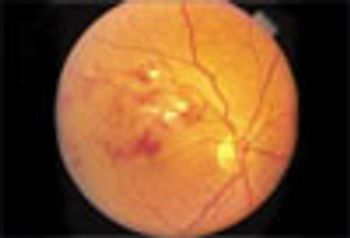
To what cause of sudden loss of vision do the funduscopic findings point?

Organizations are intensifying efforts to control this disease, the number one risk factor for disability and death in the United States and worldwide.

Recommendations consider the whole patient, the spectrum of risks and complications for the patient, and evidence-based approaches to treatment.