
The reduction in dementia is not simply the result of the drugs reducing their blood pressure.

The reduction in dementia is not simply the result of the drugs reducing their blood pressure.

Typical interventions in persons without CKD are essential. SHARP and TNT have added to our knowledge. Aggressive cholesterol lowering (probably also affecting LDL particle number as well as traditional measures of LDL) seems to afford better outcomes by lessening residual risk in those with chronic kidney disease.

Goals for HbA1C, blood pressure, and LDL-C among diabetes patients are being met by more, according to the NIH.

FDA approves 3 drugs for type 2 diabetes; African Americans undertreated for hypertension; poor participation in clincall trials; impact of restricted marketing on medical students; PCPs and radiology reporting.

It appears that the attractiveness of beta-blockers is waning for patients with heart failure and also for those with acute MI. Carvedilol is becoming a preferred agent.

Researchers found that among African American patients with uncontrolled hypertension, fewer than half were prescribed guideline-recommended first-line therapy with diuretics.

Dark chocolate, tomatoes, and grapeseed oil are just a few of the natural approaches to cardiovascular risk reduction supported by science.

Blueberries and strawberries contain high concentrations of anthocyanins, a flavonoid shown to help lower blood pressure and improve endothelial function.

The FDA requires reductions in recommended doses of zolpidem; update on the flu; new BP goals for patients with diabetes; selective use of D-Dimer for suspected DVT; new food safety standards. . . here: 5 quick summaries of medical news headlines with links out to original sources.

Here: a battle plan to address obesity-the root problem of our current epidemic of metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus-that involves kicking a sedentary lifestyle.

The benefits of antihypertensives in the elderly should be unquestioned-especially since SHEP and its revisit. Avoiding them will create more problems. But caution can be exercised with these specific measures.

Newly diagnosed hypertension in a patient whose blood pressure is 152/94 mm Hg. What agents will you consider for this patient? Beta-blockers? Think again.
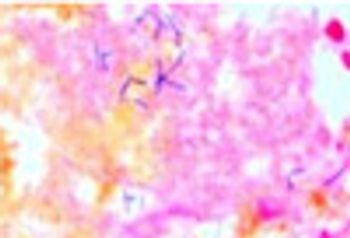
Emphysematous cholecystitis is a rare condition that is the result of infection with Clostridium perfringens and other gas-producing organisms including Escherichia coli, Bacteroides fragilis, and Klebsiella species.

More than half of adults 65 years and older have at least 3 chronic conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes mellitus, arthritis, high blood pressure, and Alzheimer disease, according to the American Geriatrics Society.

Insomnia can have serious consequences for patients who already have high blood pressure, according to a new study presented at the American Heart Association’s High Blood Pressure Research 2012 Scientific Sessions.

Hyperglycemia uncontrolled by oral antidiabetes agents alone can be complicated by drug-induced weight gain. GLP-1 agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors offer alternatives.

Hypertension is very common in people with diabetes; in this patient’s case, it may have been present for 5 to 10 years before the hyperglycemia appeared.

In addition to lifestyle changes, how would you treat this patient?

Persons with primary hyperaldosteronism and hypertension are at significantly increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. But if these patients are treated with spironolactone and reach target blood pressure, their CV outcomes are the same as those of others with essential hypertension after 6.5 years of follow-up.

Achieving sustained reductions of hyperlipidemia and blood pressure in a patient with diabetes is not impossible, but it's a challenge. A new study comparing two health systems shows which factors increase the odds of success.

The key diagnostic considerations hypokalemia, periodic paralysis, and ischemia should lead the assessment of a patient with acute generalized weakness.

Neither chlorthalidone nor spironolactone can be ignored in today's antihypertensive armamentarium. Both agents, alone or in combination, have appealing indications.

Some say chlorthalidone is superior to hydrochlorothiazide and should be used as first-line therapy in hypertension. A compelling case can be made for resurrecting this venerable drug.

A 22-year follow-up of the SHEP study cohort showed that each month of active treatment with chlorthalidone was associated with a 1-day extension of life.
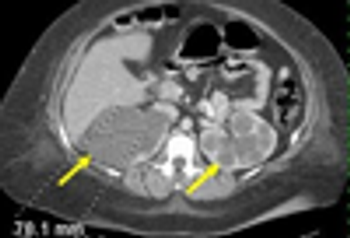
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is common. Presenting symtpoms include hypertension, hematuria, proteinuria, and renal insufficiency.