
According to the Sgarbossa criteria, the patient had an acute MI: ECG revealed a greater than 1-mm ST-segment depression in lead V2 and about 5-mm discordant ST-segment elevation in leads II, III, and aVF.

According to the Sgarbossa criteria, the patient had an acute MI: ECG revealed a greater than 1-mm ST-segment depression in lead V2 and about 5-mm discordant ST-segment elevation in leads II, III, and aVF.

Clinicians sometimes give patients a choice of medication or lifestyle changes to control blood pressure (BP) or cholesterol levels.

A 3-year-old boy was brought into the office for vague abdominal pain of 5 days’ duration. His mother stated that he had had several episodes of nonspecific pain in the abdomen that lasted a few minutes and resolved spontaneously.

A 68-year-old African American man presents for a checkup. He has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for the past 5 years but has no nephropathy and no history of cardiovascular disease. He is currently taking atorvastatin, 80 mg/d, and his low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is 80 mg/dL. His blood pressure was 148/98 mm Hg at the last visit and is now 150/98 mm Hg. What is the best treatment for him?
A 43-year-old white man presented to the emergency department with dyspnea, abdominal bloating, fever with chills, night sweats, decreased oral intake, and myalgia of 1 week's duration. He was found to have heart failure caused by systolic dysfunction. Viral myocarditis was the presumptive diagnosis after investigation for other causes.

Only 7% of patients with diabetes have reached goals for hemoglobin A1c, LDL cholesterol, and blood pressure. What can be done to help more patients achieve their goals? In this 2-part interview, Dr Edward Shahady shows how group visits can help your patients with diabetes better control their disease and reduce their risk of diabetic complications.

What is the lowest acceptable diastolic blood pressure (BP) in an elderly patient who is being treated for systolic hypertension?
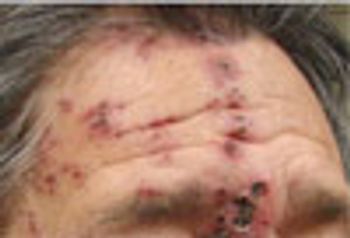
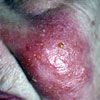
Several days earlier, a 69-year-old man had a mild headache, fatigue, and tingling and prickly facial sensations. Shortly afterward, this painful, “weepy” rash developed on his forehead, upper cheek, and nasolabial folds and vision in the right eye became blurry. The patient’s history included type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and childhood varicella.

I understand that patients with refractory hypertension have a high risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) syndrome. Can this be screened for in an office setting?

Case 1: Mr A. is a 55-year-old man who comes to your office for a routine physical examination. He is a traveling salesman and has recently gained weight. He does not exercise much and is a frequent visitor to fastfood establishments. His father had “a touch of diabetes” and died of a myocardial infarction (MI) at age 59.
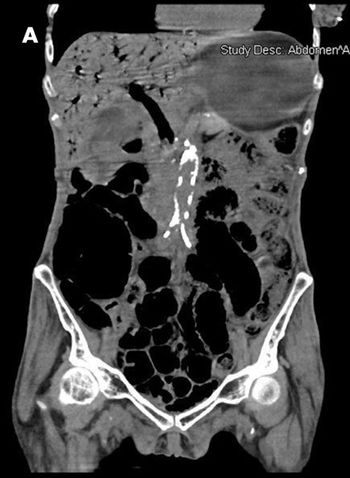
A 70-year-old woman with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (hemoglobin A1c, 12.5%) and hypertension was brought to the emergency department for evaluation of abdominal pain and loose bowel movements.
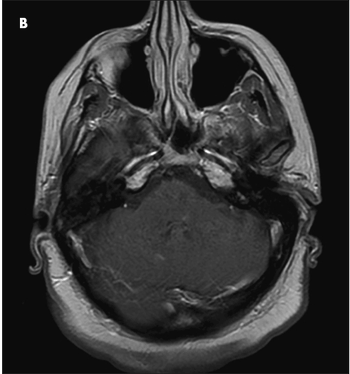
For a month, an obese 50-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension had blurry vision in both eyes. During this time, she also had ataxia and right-sided numbness. For the past 2 days, she had had horizontal, binocular diplopia with right gaze.

For 2 months, a 60-year-old man has had this pruritic eruption on his arms, legs, and trunk. It is itchy enough at times to interfere with his sleep. He has taken the same antihypertensive medication for more than a year.

A 77-year-old man of Japanese ancestry with a history of well-controlled hypertension was seen in the morning for a routine examination. His blood pressure was normal as were the results of a complete blood cell count and liver function tests. About 6 hours later, he presented to the emergency department with acute abdominal pain accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills. He denied headaches, palpitations, and diaphoresis.

The past 3 decades have seen a profound paradigmatic shift in the treatments available for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Because the disease is complicated by a variety of macrovascular and microvascular pathologies, interventions must be broad-based (tight glycemic and blood pressure [BP] control, serum lipid and urinary protein reductions). This "multifactorial" approach has proven successful.
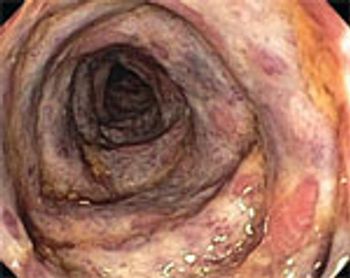
A 61–year–old man presented to the emergency department with diffuse lower abdominal pain, nausea, and severe diarrhea (20 episodes within the past 12 hours). His symptoms began the night before and had gradually worsened. He denied fever. His medical history was significant for hypertension.
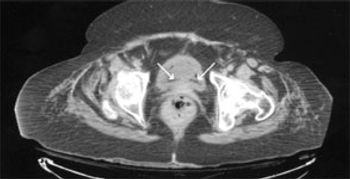
A 77-year-old woman with hypertension, diabetes mellitus with neuropathy and nephropathy, coronary artery disease, and previous stroke with residual right hemiparesis was hospitalized because of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting of sudden onset. She also reported subjective fever, dysuria, and foul-smelling urine.

My patient has hypertension, a history of a recent myocardial infarction (MI), and a resting heart rate in the 50s. Which β-blocker is preferred in this setting-or should β-blockers be avoided? -- Edwin Kellerman, MD, Merion Station, Pa
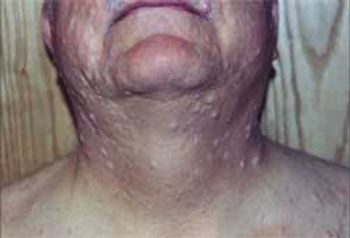
During a routine physical examination, multiple, randomly distributed, fleshcolored nodules were noted on the trunk, arms, and face of a 62-year-old man. The lesions measured 0.5 to 1.0 cm and appeared slightly pedunculated. The patient had had the lesions since he was a teenager; they were not painful. He also had hypertension, for which he was taking lisinopril (20 mg once daily).
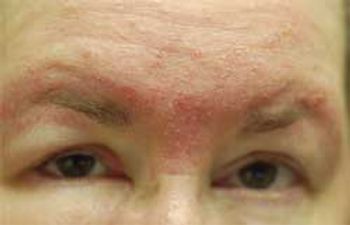
This 65-year-old woman seeks evaluation of asymptomatic swelling of her eyelids of 2 to 3 months’ duration. She has taken the same antihypertensive for years and denies any exposure history.
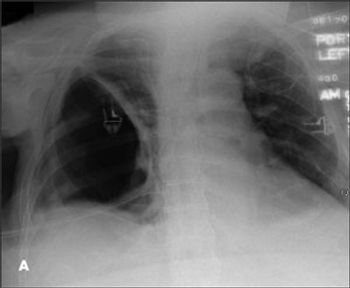
For 3 months, a 63-year-old man had experienced progressively worsening dyspnea. He denied fever, weight loss, and hemoptysis. Eight months earlier, he had had a right thoracotomy to drain a right empyema. Comorbidities included morbid obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea. However, he did not have any intrinsic lung disease.

The 1990s were an exciting decade for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The addition of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and then angiotensin receptor blockers to the antihypertensive armamentarium helped preserve renal function and decrease proteinuria in patients with CKD.

In the United States, an estimated 5 million people have heart failure and about 550,000 new cases occur each year.1 The incidence is rising as more patients survive what were once fatal myocardial infarctions (MIs). Coronary artery disease (CAD) and hypertension are the most common causes of heart failure. The less frequent causes include diabetes; viral infections; valvular heart disease; drugs (eg, doxorubicin); and postpartum, alcoholic, and familial cardiomyopathies.2,3
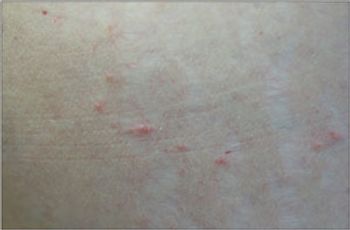
For 1 month, a 54-year-old woman has had an intensely pruritic eruption on her abdomen, arms, and anterior thighs. She has long-standing hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, which are treated with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/diuretic and an oral hypoglycemic agent.

Losing weight can significantly reduce intracranial pressure and the complications it causes, including headache and optic nerve anomalies.