
Preliminary findings being presented at the International Stroke Conference 2021 show some of the same risk factors associated with stroke in older adults also cause stroke in younger adults.

Preliminary findings being presented at the International Stroke Conference 2021 show some of the same risk factors associated with stroke in older adults also cause stroke in younger adults.

International Stroke Conference 2021: A new analysis of the landmark REDUCE-IT trial found that adding icosapent ethyl to treatment regimens that already include statins further reduces stroke risk.
Suspicion for ACS in women was lower than that for men even in the presence of significant risk factors for heart attack, study authors report.

Stroke patients are nearly 50% more likely vs heart attack patients to develop depression, according to new research being presented at the upcoming International Stroke Conference.

Using metabolomic profiling from more than 11 000 individuals, researchers identified common pathways linking seemingly unrelated diseases that often co-occur.

A new study suggests that women who experience an accelerated accumulation of abdominal fat during menopause are at greater risk of heart disease, even if their weight stays steady.

FDA approved the fixed-dose combination heart failure drug sacubitril/valsartan to reduce risk of CV death and hospitalization in patients with chronic heart failure.

To ensure COVID-19 vaccination priority for the sickest CVD patients, the ACC statement identifies highest risk conditions within CVD to aid clinician decision making.
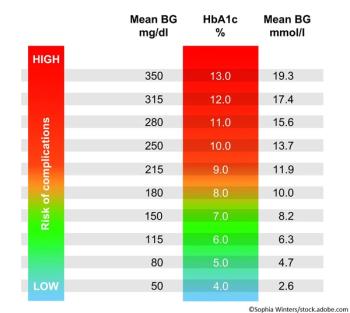
Variability in A1c during the first 2 years after T2D diagnosis is a strong predictor of CV disease; study authors note the risk may be mediated by severe hypoglycemic episodes.

Heart disease, again the leading cause of death worldwide, may remain so for many years as a result of COVID-19 pandemic conditions, says AHA Update Writing Committee Chair.

Video: George Bakris, MD says over the next 3 years there is going to be an "explosion" in the number of studies we see in heart failure, diabetic kidney disease, and CV risk in general.

The FDA approved vericiguat to reduce the risk of CV death and rehospitalization for HF in HF patients after hospital discharge or after outpatient treatment with IV diuretics.

Physical activity cannot compensate adequately for the negative impact of excess body weight on cardiometabolic health.

Thirty-day hospital readmission was found to be higher among cardiovascular patients who believed readmission was highly likely vs those who did not believe so.

People who regularly consume just 1 alcoholic drink a day are at a 16% increased risk of atrial fibrillation compared to those who do not drink alcohol at all, a new study found.

Sotagliflozin reduced CV death and hospitalization for HF in patients with T2D and acute symptomatic HF when given during or immediately after hospitalization.
The most popular features in preventive cardiology this year were interviews with thought leaders on management of diabetes, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia.

Interviews with obesity experts, short tests of clinical and guideline knowledge, and news briefs topped the popular content on obesity on Patient Care in 2020.

An FDA panel voted to recommend the expanded use of sacubitril/valsartan for patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Results of a new study suggest a simple clinical approach to assessing individuals at high risk of CHD who would benefit from targeted intervention.
A high-dose influenza vaccine was no more effective than the standard-dose vaccine at reducing the risk of severe outcomes among patients with heart disease, NIH study finds.

New research found women face a 20% increased risk of developing heart failure or dying within 5 years after their first heart attack vs men.

AHA 2020: Daily supplementation with 2000 IU of vitamin D3/day and/or 840 mg omega-3 fatty acids/day did not reduce or increase risk of incident atrial fibrillation.
AHA 2020 Virtual Scientific Sessions: Nearly one-third of racial disparities in hypertension treatment may be linked to inequities in treatment intensification, study authors suggest.

AHA 2020 Virtual Scientific Sessions: Cumulative exposure, exposure intensity, and number of household smokers in childhood all impact adult heart function, study authors found.