
Refresh your memory on findings from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME, CANVAS, CREDENCE, and DECLARE-TIMI cardiovascular outcomes trials on SGLT2 inhibitors.

Refresh your memory on findings from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME, CANVAS, CREDENCE, and DECLARE-TIMI cardiovascular outcomes trials on SGLT2 inhibitors.

A new study found adults with high blood pressure were about half as likely to have serious cardiovascular events after receiving telemonitoring vs those receiving primary care.

In episode 2 of Primary Viewpoints, lipidologist and preventive cardiologist Seth Baum, MD, discusses lipid management in preventive cardiology.

Interview: The liver disease itself, and not the associated metabolic dysfunction, may lead to CV death in these patients. Seth Baum, MD, is involved in research for a treatment.

VIDEO: Preventive cardiology is a multidisciplinary therapeutic area and primary care clinicians have the advantage of greatest patient exposure to help advance care.

VIDEO: Treatment for ASCVD patients at high risk is lagging behind the availability of powerful new therapies. And, the pandemic does not help, according to Seth Baum, MD.

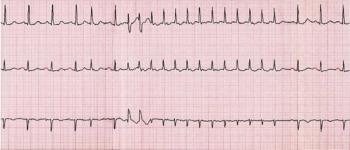
Palpitations and syncope during dinner (him); arrhythmia that looks like SVT after 2 energy drinks (her). What do the ECGs tell you?

Cardiologist Deepak Bhatt, MD, discusses factors to consider when assessing the need for cardiovascular risk management or reduction.

A key opinion leader discusses effective CV risk prevention measures, challenges to reducing adverse events, and effective patient education resources.
Deaths associated with atrial fibrillation have decreased, but it still takes an average of 2 years off a patient's life, according to a first-of-its-kind study.
This article reviews the evolving therapeutic landscape for lowering LDL-C and cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on the role of omega-3 fatty acids.

Computer-interpreted ECGs are part of SOP -- but the interpretation still needs confirmatin. See if your ECG read matches the machine in 2 cases from the ED.

Fear of contracting COVID-19 would keep more than half of Hispanics and Blacks experiencing heart attack/stroke symptoms from going to a hospital.

Hypertension is the modifiable cardiovascular disease risk factor responsible for the greatest mortality. Test what you know about management.
Patients with hypertension are complex and pose a real challenge to primary care. Brigham and Women's cardiologist Dr Naomi Fisher offers history and highlights.
Preventive cardiology and lipid specialist Seth J. Baum, MD, answers questions about the state of preventive cardiology in the midst of COVID-19.
Try these 5 questions on patient CVD risk scenarios likely to present to primary care. Find out what you know about AHA/ACC guideline-recommended strategies.

VIDEO: Obesity is a chronic, relapsing disease that threatens to neutralize, even reverse, years of progress in reducing CVD-related death. Ted Kyle, RPh, explores.

Obesity is a primary risk factor for cardiovascular disease and can also be modified with comprehensive care. Test yourself on the AHA/ACC recommendations for that care.
Cardiothoracic surgeon Brian Lima, MD spent weeks in a large metropolitan New York City ICU treating the sickest patients with COVID-19. He shares details.

Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of the Preventive Cardiology Program at Brigham and Women's Hospital, discusses the insidious role diabetes plays in cardiovascular disease.
SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are changing the type 2 diabetes treatment paradigm. We summarize the most recent data here and offer guidance on patient benefits.
Home blood pressure monitoring, performed accurately, is the key to data that will guide optimal hypertension treatment. Dr Naomi Fisher talks with Patient Care.
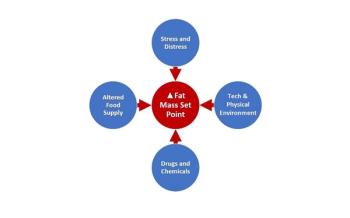
The physiology of obesity makes weight loss, by itself, unlikely to successfully treat the chronic disease of obesity. What does this mean for primary care clinical strategies?

Metabolic and bariatric surgery are deemed "elective," along with cosmetic procedures, and still widely postponed. "Resume these life-saving procedures, now," says the ASMBS.