
Primary nonadherence with anticoagulant therapy may be influenced by which DOAC is prescribed, age, and diagnosis of several chronic diseases, a new study found.


Primary nonadherence with anticoagulant therapy may be influenced by which DOAC is prescribed, age, and diagnosis of several chronic diseases, a new study found.
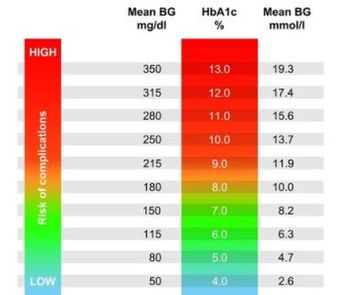
For individuals with A1c of 6.4-6.5%, just below the threshold for diabetes, risk of MACE was higher than for any other subgroup with A1c values ranging from 5.8-6.8%.

Heart failure drugs in the pipeline now number more than 100 and include familiar names plus dozens of new ones. Get a top-line look at 6 of the most promising.

Results of a GALACTIC-HF post-hoc analysis suggest a role for omecamtiv mecarbil in an HF population that remains difficult to treat effectively.

Advances in heart failure management, including inroads in treatment for HFpEF, are happening fast. Try 8 questions to find out how well you’ve been following the news.

Novel peer-reviewed study found that a mobile hypertension self-management program can support long-term BP control and very high BP detection.

A survey of adults aged 50-80 years with hypertension and/ or related comorbidities found even among those with a BP monitor at home, less than 50% checked BP at least once a week.

SGLT-2 inhibitors have proven effective in disease modification as well as symptom improvement across HF phenotypes and severity. Get a quick summary of the research.
The USPSTF shift to a more conservative recommendation on use of aspirin compared to its 2016 stance is based on new RCT data and net benefit modeling.
Iron deficiency can't be causally linked to CHD yet, but evidence is accumulating for the association, according to authors of a new European study.
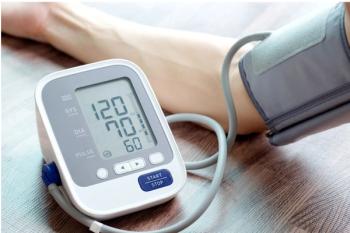
Clinical guidelines recommend home or ambulatory BP monitoring to diagnose hypertension. New research sheds light on what patients prefer and will adhere to.
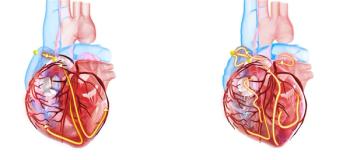
The temporal connection of atrial fibrillation and risk of ischemic stroke provides support for short-duration oral anticoagulation, said study authors.

EASD 2021: Patients with metabolically healthy obesity are nearly 33% more likely to develop heart failure and atrial fibrillation than healthy persons of normal weight, suggests new analysis.
Hypertension in women over age 70 years and men younger than 50 years requires closer monitoring, even if patients are on treatment, say authors.

A pattern of nocturnal reverse-dipping blood pressure in persons with type 1 or 2 diabetes put them at more than twice the risk of all-cause mortality, according to new research.

EASD 2021: For persons who have had obesity, returning to a healthy weight may reduce risk for hypertension and dyslipidemia, and modestly for diabetes.

EASD 2021: Women with type 2 diabetes were less likely to meet targets for CV risk management vs men but at lower risk for future CV events, a new study found.
Helicobacter pylori infection in early-middle-aged adults was associated with higher BMI, triglyceride levels, carotid plaque formation, and carotid intima-media thickness.
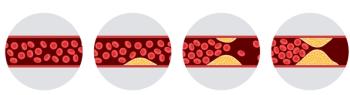
Clinical decisions on LDL-C management currently rely on a measure at one time point, typically middle age. A new study suggests burden begins early and so should assessment.
A new AHA scientific statement suggests metabolic surgery and weight-loss medications may reduce the long-term effects of obesity-related hypertension.

New hypertension research looks at stress hormones in early disease, the Quadpill as first Rx, tight BP control for older adults--for a start. We recap 8 new studies.
CCTA identified atherosclerosis in >40% of middle-aged adults without known coronary heart disease, report Swedish investigators; significant stenosis was found in another 5.2%.

Dapagliflozin adds substantial improvements in symptoms, exercise function to demonstrated disease-modifying properties for patients with HFpEF.

Identifying white coat and masked hypertension is essential for prevention of CV morbidity and mortality. Review the ACC/AHA recommendations on how to detect and manage.

Each doubling of levels of 4 stress hormones was associated with a 21-31% increase in risk of developing hypertension over a median 6.5-year follow-up.