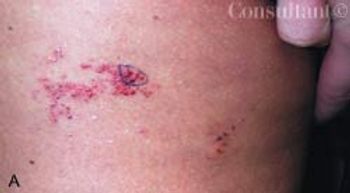
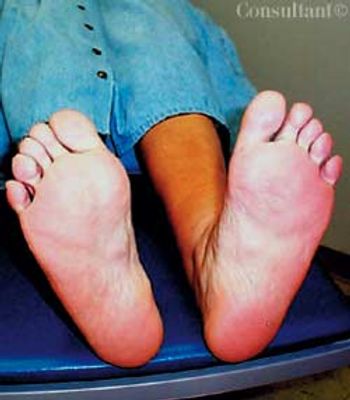
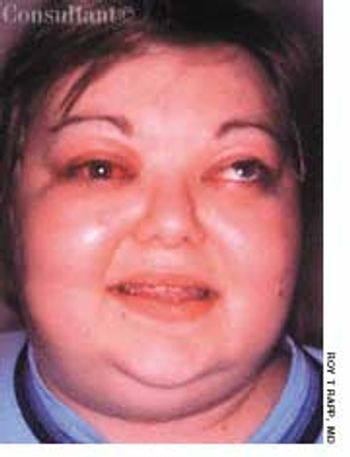
Persons with severe mental illnesses (SMI), such as schizophrenia, are at increased risk for comorbid conditions- including type 2 diabetes-independent of therapy. SMI sufferers especially at risk for type 2 diabetes are women, African Americans, and persons older than 45 years. Among the possible causes of increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes are such schizophrenia-associated conditions as impaired glucose tolerance, overweight, obesity, inadequate nutrition, lack of exercise, and inadequate self-care. Other obstacles to good health care among patients with schizophrenia include impaired communication ability, denial of illness, social withdrawal, and undertreatment because of comorbid conditions. Different antipsychotic medications may also contribute to preexisting insulin resistance or glucose intolerance. Clinicians can optimize care by understanding the most significant barriers for each patient and incorporating this knowledge into an active treatment plan.