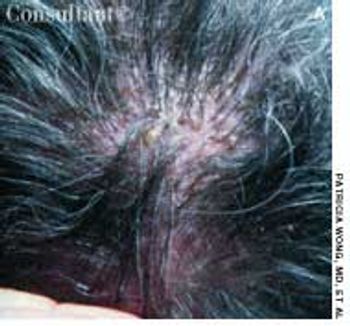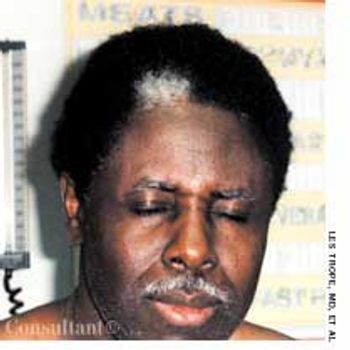
During a routine physical examination, a white forelock was noted on a 54-year-old man. The patient stated that the discolored patch of hair had been present since adolescence. Other than mild hearing loss, he had no significant personal or family medical history.