
How critical-and cost-effective-is in-officepulmonary function equipment for the primarycare practitioner?

How critical-and cost-effective-is in-officepulmonary function equipment for the primarycare practitioner?

A 41-year-old woman has had a 2-week bout of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.Her history includes chronic hepatitis C and alcohol abuse. She also has orthostatichypotension. A baseline ECG is obtained.
For 2 months, a 47-year-old woman experienced constipation, weakness, fatigue, and dry skin. She also complained of moderate weight gain and menorrhagia during the same period. The patient took no medications and denied any allergies.

A 78-year-old man presented to theemergency department with a 3-weekhistory of progressive shortness of breathand cough with blood-streaked, yellowishsputum. The patient had dyspnea onexertion limited to 2 blocks, 2-pilloworthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea,and nocturia. Neither fever norchills were present. He had lost 7.2 kg(16 lb) during the last year.

Smoking-related diseases have reached epidemic levelsamong women in the United States. Since 1980, neoplastic,cardiovascular, respiratory, and pediatric diseases attributableto smoking-as well as cigarette burns-havebeen responsible for the premature deaths of 3 millionAmerican women and girls. Lung cancer is now the leadingcause of cancer-related deaths among US women; itsurpassed breast cancer in 1987.1

Calcium channel blockersare commonly prescribedto treat severalcardiovascular diseasesand may be helpful inother conditions, such as migraineand bipolar disorder.1 These agentsare associated with numerous clinicallysignificant drug interactions.1-3While some of these interactions,such as the effect of verapamil onserum digoxin concentrations, arewell-known, others are not widely recognized-yet warrant attention.
A 48-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with deep venous thrombosis of the right leg. She had a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which was in remission. The patient had been a heavy smoker for many years.

A 69-year-old retired accountant presents with a 2-month history of daily headaches. The pain is moderate, constant,global, pressure-like, and occasionally pulsating; it is sometimes exacerbated when the patient lies down. He denies nauseaor vomiting, ocular symptoms, weakness, or sensitivity to light. His wife reports that years ago he experienced throbbingheadaches regularly.

During a routine office visit, a 64-year-old woman who has had type 2 diabetesfor more than 10 years complains of increased pedal edema. The edema is minimalon awakening and worsens throughout the day.

My patient is a 42-year-old woman who experienced a nonblanching, purpuricrash and edema of the lower legs after she started taking nifedipine (Figure).

Although acute low back pain usuallyresolves within 6 weeks-with or withouttreatment-the pain may signal asignificant neurologic or life-threateningdisease that warrants immediateintervention.

More than1.8 millioncardiaccatheterizationsandat least 600,000 percutaneoustransluminal coronaryangioplasty (PTCA)procedures are performedin the United States annually.1 The use of these diagnosticand interventionalmodalities continues togrow even as financial constraintsincrease. Yet formany patients with coronaryartery disease (CAD),medical therapy may be anappropriate option.

Drs Sonia Arunabh and K. Rauhilla’s case of a 62-year-old woman with Raynaud’sphenomenon (CONSULTANT, September 15, 2001, page 1526) offers one ofthe finest photographs of this condition that I have seen (Figure).

A 72-year-old man sought medical evaluationafter he awoke and was unableto open his right eyelid (A). He deniedpain, recent trauma, and diplopia. Thispatient’s history included well-controlledhypertension and hypercholesterolemia,for which he was taking atorvastatin.He did not have diabetes.
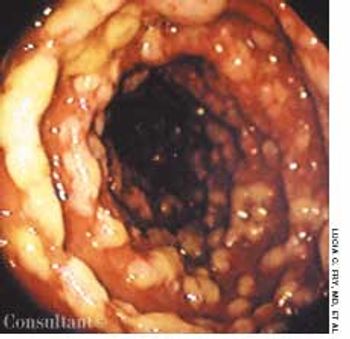
For 2 days, a 68-year-old woman had watery, yellowish diarrhea with mucus and left lower quadrant pain. Her medical history included hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and congestive heart failure (CHF); she had left the hospital 5 days earlier following treatment of an exacerbation of CHF with intravenous furosemide and sodium and fluid restriction. The patient was taking furosemide, lisinopril, and glipizide; she denied any recent antibiotic therapy.
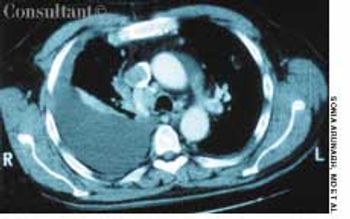
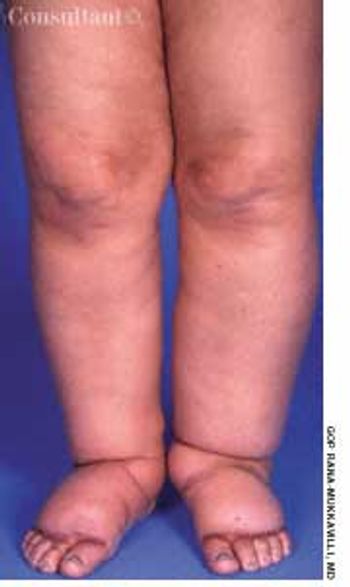
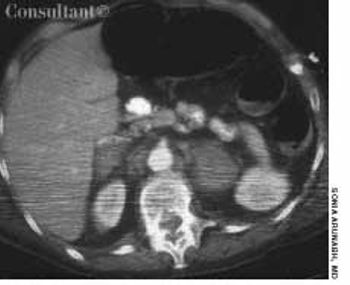
A 64-year-old woman with a history of diabetes, hypertension, and lymphoma was admitted to the hospital with a dull headache, conjunctival congestion, and slight dyspnea. Her pulse rate was 96 beats per minute; blood pressure, 146/68 mm Hg; and respiration rate, 22 breaths per minute. She also had increased jugular venous distention; cardiovascular and chest examination findings were normal. Edema of both arms and dilated blood vessels on the anterior chest wall were noted.

A 63-year-old woman seeks evaluation of a persistent, rough, red area onthe dorsum of her left index finger. The lesion has been present for severalmonths. The patient’s manicurist is convinced it is a wart.
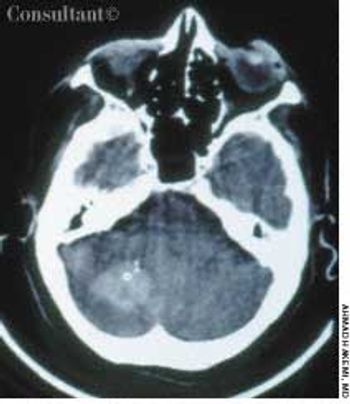
A 65-year-old woman with a long history of hypertension treated with metoprolol and felodipine complained of dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting of acute onset. Her blood pressure was 220/110 mm Hg. She was drowsy and unable to stand or walk.

In their article, “Dyslipidemia in Patients With CAD: How to Make Best Useof Drug Therapy” (CONSULTANT, October 2000, page 2097), Drs Harry Yu,Richard Pasternak, and Geoffrey Ginsberg discuss the adverse effects associatedwith statin therapy, including myositis.

Heart failure(HF), the mostcommon Medicarediagnosisrelatedgroup,has a significant and growingimpact on health careresources. The incidenceof HF has tripled during thelast decade. Almost 5 millionAmericans have HF, and anestimated 500,000 new casesare diagnosed yearly. Thelifetime risk of HF is about20%.1 Drug therapy has improvedconsiderably in recentyears, but the magnitudeand severity of theproblem has created a needfor newer therapies--particularlysince HF is associatedwith an increased risk ofsudden death and a diminishedquality of life.2

A 58-year-old man recently underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)surgery after emergent cardiac catheterization for a myocardial infarction revealeddiffuse 3-vessel disease.

Many of my older women patients think theyare at much higher risk for breast cancer thancoronary heart disease (CHD). How can we raise women'sawareness about their risks of CHD and therebyencourage them to take measures to prevent it?

Dr Gregory Rutecki's interactive teaching case, “A Middle-Aged Man WithPolyuria: The Initial Visit” (CONSULTANT, March 2001, page 357), provided awelcome opportunity for me to review the care I provide to my patients with type 2diabetes, who comprise a very large percentage of my practice.
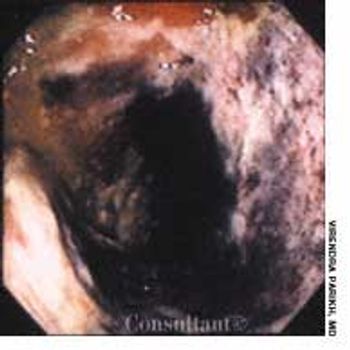
For 2 days, a 79-year-old man with a history of congestive heart failure experienced abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dark red rectal bleeding. The pain was localized to the left lower quadrant.

Q:Should I avoid angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in mypatients with progressive renal insufficiency?