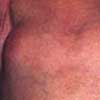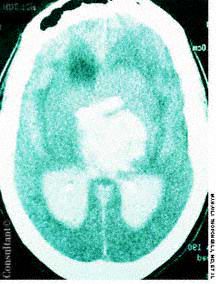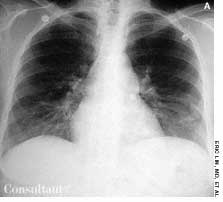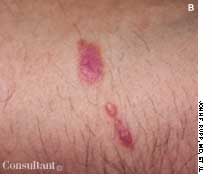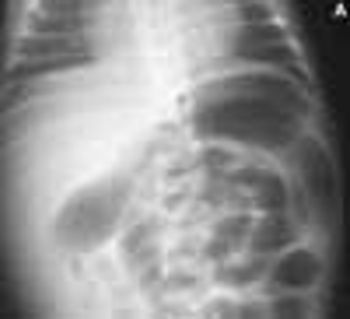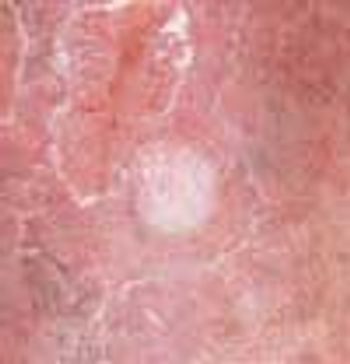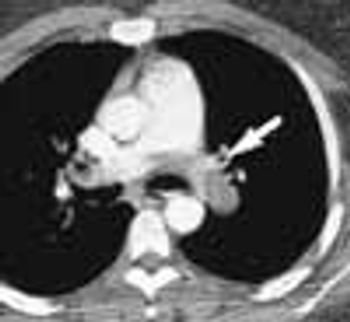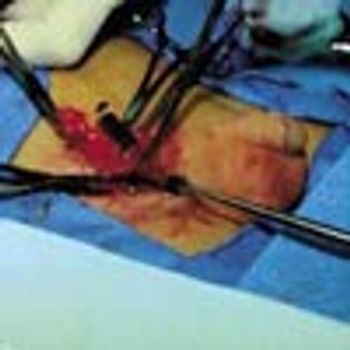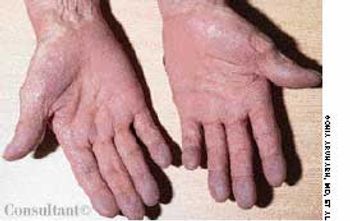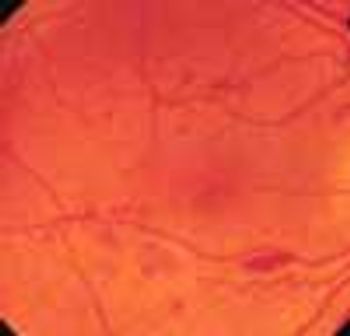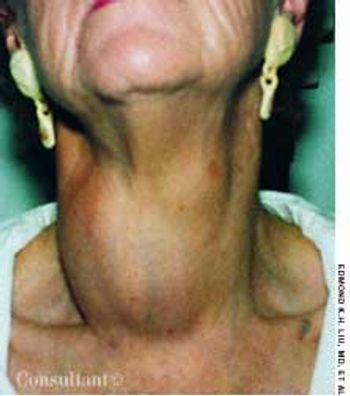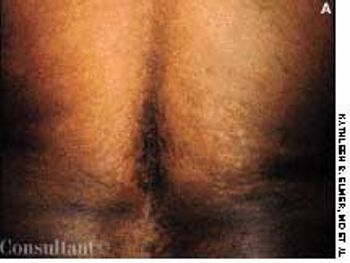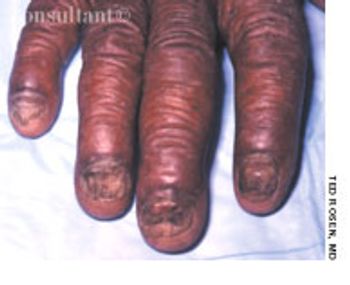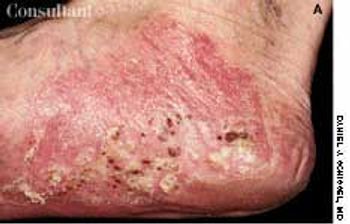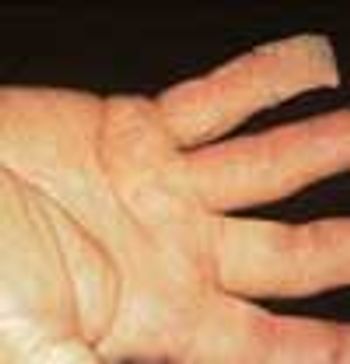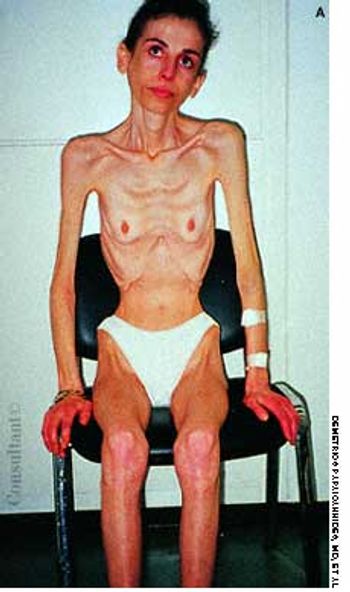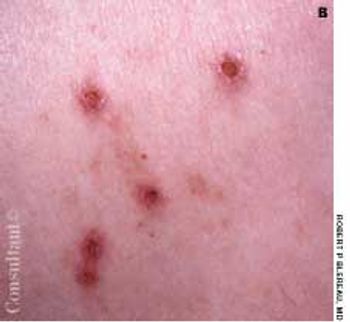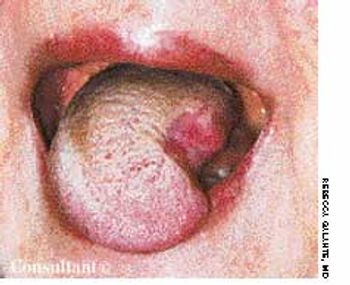
The initial complaint of a 79-year-old woman was of mild headache, neck pain, and sore throat. She had a history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and heavy cigarette smoking. Examination by an otolaryngologist, which included laryngoscopy, revealed no abnormalities. Three weeks later, the patient's throat and neck pain became more severe. She had no arthralgias, visual loss, fever, or worsening head pain.