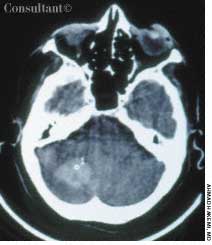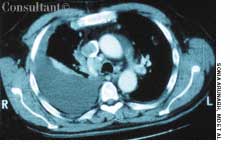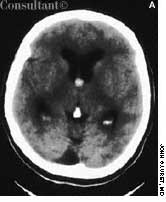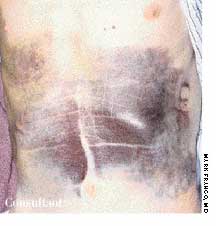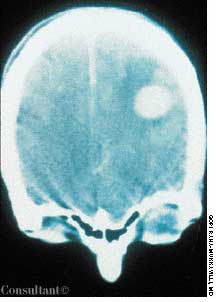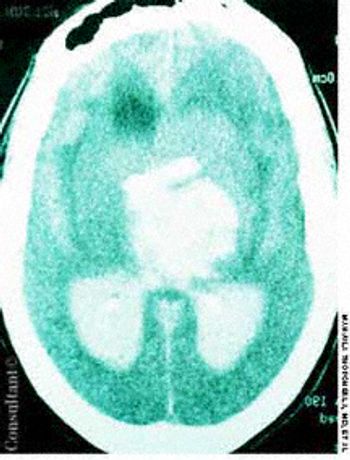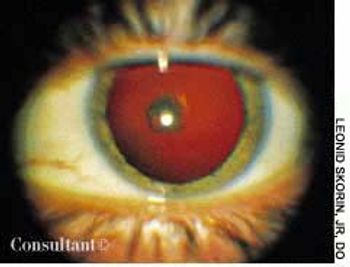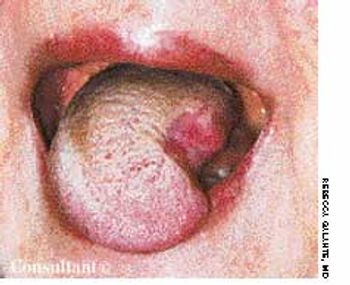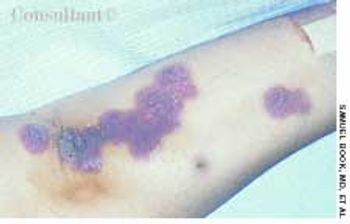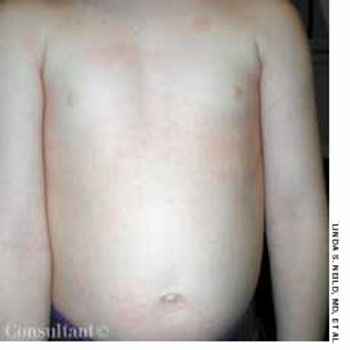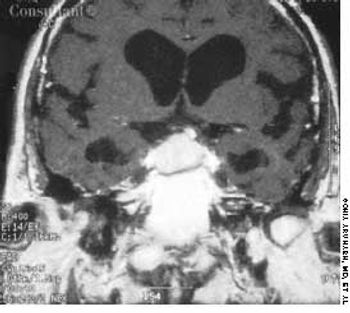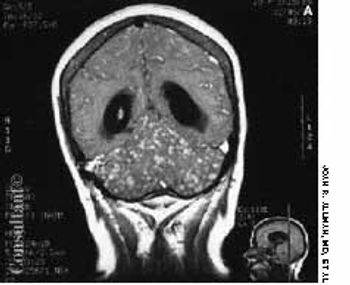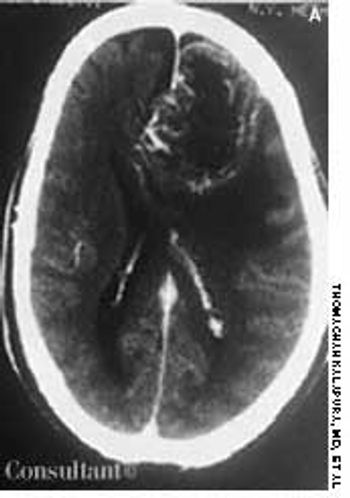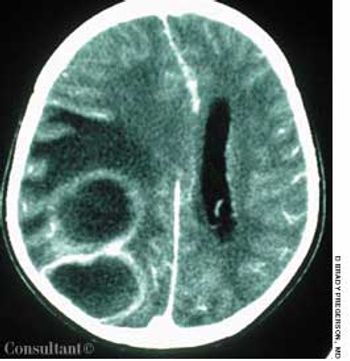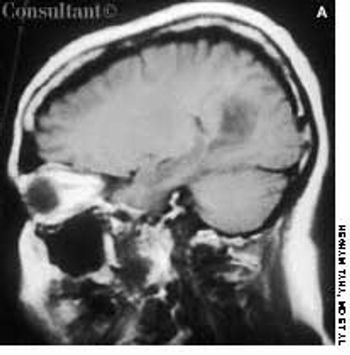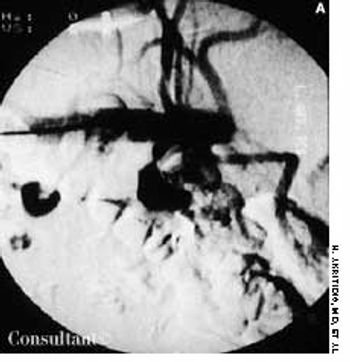
The wife of an 82-year-old man with Alzheimer's disease was concerned about her husband's poor posture. According to the woman, the patient had never sustained a back injury and had always maintained a sedentary lifestyle. He never smoked cigarettes and did not use alcohol. His history included multiple transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).